Notes to the Financial Statements - Other Disclosures
59. Contingent Liabilities and Commitments
Contingent liabilities are possible obligations whose existence will be confirmed only by uncertain future events or present obligations where the transfer of economic benefit is not probable or cannot be readily measured as defined in the Sri Lanka Accounting Standard – LKAS 37 on “Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets”.
To meet the financial needs of customers, the Bank enters into various irrevocable commitments and contingent liabilities. These consist of financial guarantees, letters of credit and other undrawn commitments to lend. Letters of credit and guarantees commit the Bank to make payments on behalf of customers in the event of a specific act, generally related to the import or export of goods. Guarantees and standby letters of credit carry a similar credit risk to loans.
Contingent liabilities are not recognised in the Statement of Financial Position but are disclosed unless its occurrence is remote.
Operating lease commitments of the Group (as a lessor and as a lessee) form part of commitments and pending legal claims against the Group form part of contingencies.
Even though these obligations may not be recognised on the Statement of Financial Position, they do contain credit risk and are therefore part of the overall risk of the Bank as disclosed in Note 59.1 to the Financial Statements.
In the normal course of business, the Bank makes various irrevocable commitments and incurs certain contingent liabilities with legal recourse to its customers. Even though these obligations may not be recognised on the date of the Statement of Financial Position, they do contain credit risk and are therefore form part of the overall risk profile of the Bank.
|
|
|
GROUP |
BANK |
| As at December 31, |
|
|
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
|
Note |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Contingencies |
|
|
438,543,821 |
365,862,605 |
438,454,025 |
365,853,920 |
| Guarantees |
|
|
64,869,807 |
33,267,170 |
64,869,608 |
33,258,485 |
| Performance bonds |
|
|
30,604,509 |
22,553,060 |
30,601,521 |
22,553,060 |
| Documentary credits |
|
|
45,146,266 |
36,222,394 |
45,078,313 |
36,222,394 |
| Other contingencies |
59.1 |
|
297,923,239 |
273,819,981 |
297,904,583 |
273,819,981 |
| Commitments |
|
|
126,734,000 |
132,705,895 |
126,340,860 |
132,450,607 |
| Undrawn commitments |
59.2 |
|
124,977,782 |
131,628,622 |
124,594,675 |
131,381,356 |
| Capital commitments |
59.3 |
|
1,756,218 |
1,077,273 |
1,746,185 |
1,069,251 |
| Total |
|
|
565,277,821 |
498,568,500 |
564,794,885 |
498,304,527 |
59.1 Other contingencies
|
GROUP |
BANK |
| As at December 31, |
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Forward exchange contracts: |
68,436,909 |
70,646,854 |
68,436,909 |
70,646,854 |
| Forward exchange sales |
24,380,254 |
26,084,323 |
24,380,254 |
26,084,323 |
| Forward exchange purchases |
44,056,655 |
44,562,531 |
44,056,655 |
44,562,531 |
| Interest Rate Swap agreements/Currency Swaps: |
164,800,830 |
158,012,034 |
164,800,830 |
158,012,034 |
| Interest rate swaps |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Currency swaps |
164,800,830 |
158,012,034 |
164,800,830 |
158,012,034 |
| Others: |
64,685,500 |
45,161,093 |
64,666,844 |
45,161,093 |
| Acceptances |
40,336,138 |
25,281,037 |
40,321,501 |
25,281,037 |
| Bills for collection |
23,310,642 |
19,260,765 |
23,306,623 |
19,260,765 |
| Stock of Travellers’ Cheques |
1,030,549 |
616,341 |
1,030,549 |
616,341 |
| Bullion on consignment |
8,171 |
2,950 |
8,171 |
2,950 |
| Subtotal |
297,923,239 |
273,819,981 |
297,904,583 |
273,819,981 |
59.2 Undrawn commitments
|
GROUP |
BANK |
| As at December 31, |
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| On direct advances |
105,053,514 |
97,459,750 |
104,670,407 |
97,212,484 |
| On indirect advances |
19,924,268 |
34,168,872 |
19,924,268 |
34,168,872 |
| Subtotal |
124,977,782 |
131,628,622 |
124,594,675 |
131,381,356 |
59.3 Capital commitments
The Group has commitments for acquisition of property, plant and equipment and intangible assets incidental to the ordinary course of business which have been approved by the Board of Directors, the details of which are as follows:
|
GROUP |
BANK |
| As at December 31, |
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Commitments in relation to property, plant and equipment |
1,539,657 |
647,677 |
1,529,624 |
647,677 |
| Approved and contracted for |
1,425,307 |
511,667 |
1,415,274 |
511,667 |
| Approved but not contracted for |
114,350 |
136,010 |
114,350 |
136,010 |
| Commitments in relation to intangible assets |
216,561 |
429,596 |
216,561 |
421,574 |
| Approved and contracted for |
216,561 |
429,596 |
216,561 |
421,574 |
| Approved but not contracted for |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Subtotal |
1,756,218 |
1,077,273 |
1,746,185 |
1,069,251 |
59.4 Contingent liabilities and commitments of subsidiaries and associates
59.4 (a) Contingent liabilities and commitments of subsidiaries
Contingent liabilities and commitments of the subsidiary, Commercial Bank of Maldives Private Limited have been included in the Consolidated Financial Statements of the Group while other subsidiaries of the Group do not have any contingencies or commitments as at the reporting date.
59.4 (b) Contingent liabilities and commitments of associates
The associates of the Group do not have any contingencies as at the reporting date.
60. Net Assets Value per Ordinary Share
|
GROUP |
BANK |
| As at December 31, |
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
| Amounts used as the numerator: |
|
|
|
|
| Total equity attributable to equity holders of the Bank (Rs. ’000) |
107,994,800 |
78,992,310 |
107,099,360 |
78,353,664 |
| Number of ordinary shares used as the denominator: |
|
|
|
|
| Total number of shares |
995,899,302 |
890,734,540 |
995,899,302 |
890,734,540 |
| Net assets value per share (Rs.) |
108.44 |
88.68 |
107.54 |
87.97 |
61. Litigation Against the Bank
Litigation is a common occurrence in the banking industry due to the nature of the business. The Bank has an established protocol for dealing with such legal claims. In respect of pending legal claims where the Bank had already made provisions for possible losses in its Financial Statements or has a realisable security to cover the damages are not included below as the Bank does not expect cash outflows from such claims. However, further adjustments are made to the Financial Statements if necessary on the adverse effects of legal claims based on the professional advice obtained on the certainty of the outcome and also based on a reasonable estimate.
Set out below are the unresolved legal claims against the Bank as at December 31, 2017 for which, adjustments to the Financial Statements have not been made due to the uncertainty of its outcome. In addition, there are cases filed against the Bank that has not been listed here on the basis of non-materiality to operations, aggrieved party had obtained injunctions prior to acquiring the property by the Bank etc.
- Court action has been initiated by a customer in High Court proceeding No. 236/2011/MR, challenging the Bank on transfer of title of a vehicle upon settlement of a lease facility. The Bank had transferred the title of a vehicle in the name of a relative of the customer on the strength of a letter issued by him which is now being disputed. The value of the action is Rs. 3.500 Mn. Plaintiff and the 1st defendant have closed their case. Evidence of an officer of the Bank was led and further trial fixed for March 28, 2018.
- Court action has been initiated by a customer in District Court, Colombo under proceeding No. DMR 3/2014 for Rs. 14.000 Mn. to recover a sum of Rs. 13.063 Mn. including interest on cheques paid with a fraudulent signature. The case which was initially filed at the District Court was later referred to the Commercial High Court under case No. 315/2015/MR. The matter is fixed for trial on June 13, 2018.
- Court action has been initiated in District Court, Colombo under case No. 03034/14/DMR to claim a sum of Rs. 27.870 Mn. being the total amount withdrawn from the Company account with forged signatures by an employee of the company in a number of transactions during a period of two years. Further trial fixed for May 25, 2018.
- Court action has been initiated in District Court, Colombo under proceeding No. DMR/974/2016 to recover a sum of Rs. 26.237 Mn. together with interest as damages incurred by the plaintiff due to the delay by the Bank in refunding the amount with regard to a duplicated telegraphic transfer for USD 25,000. Further trial fixed for May 21, 2018.
- Court action has been initiated in District Court, Colombo under proceeding No. DMR/2274/2015 to recover a sum of Rs. 3.374 Mn. as parking charges and interest thereon due to a dispute over parking facility provided to the Bank. Trial is due on March 29, 2018.
- Court action has been initiated District Court, Kaduwela under proceeding No. 584/L for Rs. 15.000 Mn. and interest thereon in seeking declaration that the plaintiff is the lawful owner of the property mortgaged by her daughter as security for a loan (currently in the past-due section) obtained from the Bank. Replication on February 23, 2018.
- Court action has been initiated by a third party in District Court Colombo under proceeding No. DMR/873/17 to recover a sum of Rs. 15.300 Mn. as damages for accepting three stale cheques amounting to Rs. 2.500 Mn. drawn by the plaintiff and deposited to an account of a customer, which was returned as “Account Closed”. Customer has taken criminal action against the plaintiff in this regard and the latter had initiated action against the Bank successively. Answer by the Bank due on May 8, 2018.
- An appeal was filed by the Bank under proceedings No. HCALT 405/2014 in Provincial High Court of the Eastern Province against the order of the Labour Tribunal for payment of compensation and reinstatement in employment of an outsourced office helper. The office helper too filed a case in Provincial High Court in proceedings No. HCALT 404/2014 refusing compensation and asking for reinstatement. Appeal made by the Bank was dismissed and case filed by outsourced office helper was decided in favour of him. Bank has appealed in the Supreme Court against the judgement of both cases under proceeding No. SC/SPL/LA/220/15 and SC/SPL/LA/221/15. Next hearing of the cases fixed for June 1, 2018.
- Court action has been initiated in Colombo High Court under proceedings No. 112/2005 (1) to claim Rs. 5.584 Mn. and Rs. 10.000 Mn. as damages for disposing of shares owned by the plaintiff which were held under lien to the Bank. Plaintiff alleges that the transaction has taken place without obtaining her consent. Judgement was delivered in favour of the Plaintiff. Bank has appealed in the Supreme Court (Appeal No. 09/2010) against the judgement delivered. Appeal is fixed for argument on May 11, 2018.
- Court action has been initiated by a customer in Colombo High Court under proceedings No. 36/96 (1) to claim a sum of Rs. 183.050 Mn. regarding a forward exchange contract. Judgement was delivered in favour of the Bank dismissing the plaintiff’s action, but the plaintiff has appealed against the judgement in the Supreme Court (Appeal No. 38/2006). Next hearing on February 26, 2018.
- Court action has been initiated in the Commercial High Court of the Western Province under proceedings No. 571/2008/MR to prevent the Bank from exercising the inherent rights of the Bank to set-off a deposit of the plaintiff amounting to USD 15.000 Mn. against a sum due from the plaintiff in terms of a hedging agreement. Commercial High Court issued the judgement in favour of the Bank and dismissed plaintiff’s application for an interim injunction. Presently the case is at the Trial stage. Further trial fixed for March 7, 2018.
62. Maturity Analysis
Group
(i) Remaining contractual period to maturity as at the date of Statement of Financial Position of the assets employed by the Group
is detailed below:
| As at December 31, |
Up to 3
months |
3 to 12
months |
1 to 3
years |
3 to 5
years |
More than
5 years |
Total as at
31.12.2017 |
Total as at
31.12.2016 |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Interest earning assets: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Financial assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Cash and cash equivalents |
3,660,584 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
3,660,584 |
8,291,413 |
| Balances with Central Banks |
1,632,454 |
263,830 |
– |
4,607 |
– |
1,900,891 |
560,669 |
| Placements with banks |
17,633,269 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
17,633,269 |
11,718,499 |
| Securities purchased under resale agreements |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Derivative financial assets |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Other financial instruments – Held for trading |
4,096,168 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
4,096,168 |
4,693,989 |
| Loans and receivables to banks |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Loans and receivables to other customers |
232,293,546 |
199,536,025 |
171,769,829 |
94,461,959 |
44,382,771 |
742,444,130 |
620,129,488 |
| Financial investments – Available for sale |
13,224,706 |
67,787,547 |
59,124,910 |
14,229,518 |
– |
154,366,681 |
159,642,243 |
| Financial investments – Held to maturity |
6,966,556 |
12,785,739 |
12,885,249 |
29,661,652 |
7,066,600 |
69,365,796 |
63,626,598 |
| Financial investments – Loans and receivables |
2,521,780 |
5,188,975 |
16,430,329 |
24,571,393 |
– |
48,712,477 |
51,824,026 |
| Total interest earning assets as at 31.12.2017 |
282,029,063 |
285,562,116 |
260,210,317 |
162,929,129 |
51,449,371 |
1,042,179,996 |
|
| Total interest earning assets as at 31.12.2016 |
278,177,314 |
177,445,705 |
270,732,533 |
114,198,779 |
79,932,594 |
|
920,486,925 |
| Non-interest earning assets: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Financial assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Cash and cash equivalents |
31,012,840 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
31,012,840 |
24,632,814 |
| Balances with central banks |
26,999,348 |
14,321,349 |
783,669 |
730,063 |
811,029 |
43,645,458 |
43,374,589 |
| Placements with banks |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Securities purchased under resale agreements |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Derivative financial assets |
959,937 |
1,374,599 |
– |
– |
– |
2,334,536 |
1,052,829 |
| Other financial instruments – Held for trading |
314,745 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
314,745 |
293,809 |
| Loans and receivables to banks |
– |
– |
640,512 |
– |
– |
640,512 |
624,458 |
| Loans and receivables to other customers |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Financial investments – Available for sale |
– |
– |
– |
17,491 |
529,471 |
546,962 |
450,279 |
| Financial investments – Held to maturity |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Financial investments – Loans and receivables |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Non-financial assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Investments in subsidiaries |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Investments in associates |
– |
– |
– |
– |
109,844 |
109,844 |
108,859 |
| Property, plant and equipment |
– |
– |
– |
– |
16,317,044 |
16,317,044 |
11,569,666 |
| Intangible assets |
– |
– |
– |
– |
1,251,226 |
1,251,226 |
1,132,669 |
| Leasehold property |
– |
– |
– |
– |
104,516 |
104,516 |
105,968 |
| Deferred tax assets |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
668,150 |
| Other assets |
12,335,522 |
257,173 |
1,245,002 |
506,177 |
3,019,103 |
17,362,977 |
16,482,559 |
| Total non-interest earning assets as at 31.12.2017 |
71,622,392 |
15,953,121 |
2,669,183 |
1,253,731 |
22,142,233 |
113,640,660 |
|
| Total non-interest earning assets as at 31.12.2016 |
64,361,841 |
14,616,440 |
3,826,664 |
991,974 |
16,699,730 |
|
100,496,649 |
| Total assets – as at 31.12.2017 |
353,651,455 |
301,515,237 |
262,879,500 |
164,182,860 |
73,591,604 |
1,155,820,656 |
|
| Total assets – as at 31.12.2016 |
342,539,155 |
192,062,145 |
274,559,197 |
115,190,753 |
96,632,324 |
|
1,020,983,574 |
| Percentage – as at 31.12.2017 (*) |
30.60 |
26.09 |
22.74 |
14.20 |
6.37 |
100.00 |
|
| Percentage – as at 31.12.2016 (*) |
33.56 |
18.81 |
26.89 |
11.28 |
9.46 |
|
100.00 |
(*) Total assets of each maturity bucket as a percentage of total assets employed by the Group.
(ii) Remaining contractual period to maturity as at the date of Statement of Financial Position of the liabilities and shareholders’ funds employed by the Group is detailed below:
|
Up to 3
months |
3 to 12
months |
1 to 3
years |
3 to 5
years |
More than
5 years |
Total as at
31.12.2017 |
Total as at
31.12.2016 |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Interest-bearing liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Financial liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Due to banks |
33,084,091 |
4,622,936 |
13,243,490 |
1,086,634 |
41,224 |
52,078,375 |
67,012,968 |
| Derivative financial liabilities |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Securities sold under repurchase agreements |
35,806,750 |
10,978,972 |
2,746,663 |
– |
– |
49,532,385 |
69,628,961 |
| Other financial liabilities – Held for trading |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Due to other customers/deposits from customers |
456,843,445 |
290,068,614 |
18,492,159 |
13,050,450 |
13,783,280 |
792,237,948 |
685,709,264 |
| Other borrowings |
657,813 |
2,091,720 |
5,021,093 |
7,503,789 |
8,511,679 |
23,786,094 |
9,270,154 |
| Subordinated liabilities |
203,326 |
314,552 |
– |
9,477,720 |
15,170,326 |
25,165,924 |
24,849,539 |
| Total interest-bearing liabilities as at 31.12.2017 |
526,595,425 |
308,076,794 |
39,503,405 |
31,118,593 |
37,506,509 |
942,800,726 |
|
| Total interest-bearing liabilities as at 31.12.2016 |
506,171,295 |
264,521,678 |
32,826,512 |
23,143,483 |
29,807,918 |
|
856,470,886 |
| Non-interest-bearing liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Financial liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Due to banks |
8,166,517 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
8,166,517 |
4,085,423 |
| Derivative financial liabilities |
2,488,462 |
1,185,570 |
– |
– |
4,462 |
3,678,494 |
1,515,035 |
| Securities sold under repurchase agreements |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Other financial liabilities – Held for trading |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Due to other customers/deposits from customers |
65,032,033 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
65,032,033 |
57,601,349 |
| Other borrowings |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Subordinated liabilities |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Non-financial liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Current tax liabilities |
857,023 |
3,345,827 |
– |
– |
– |
4,202,850 |
3,464,682 |
| Deferred tax liabilities |
472,934 |
153,861 |
588,908 |
261,930 |
2,087,582 |
3,565,215 |
– |
| Other provisions |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
1,874 |
| Other liabilities |
3,354,484 |
9,738,767 |
2,943,111 |
1,374,896 |
2,096,857 |
19,508,115 |
18,028,902 |
| Equity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Stated capital |
– |
– |
– |
– |
37,143,541 |
37,143,541 |
24,978,003 |
| Statutory reserves |
– |
– |
– |
– |
6,492,552 |
6,492,552 |
5,647,993 |
| Retained earnings |
– |
– |
– |
– |
5,086,609 |
5,086,609 |
4,553,778 |
| Other reserves |
– |
– |
– |
– |
59,272,098 |
59,272,098 |
43,812,536 |
| Non-controlling interest |
|
|
|
|
871,906 |
871,906 |
823,113 |
| Total non-interest-bearing liabilities as at 31.12.2017 |
80,371,453 |
14,424,025 |
3,532,019 |
1,636,826 |
113,055,607 |
213,019,930 |
|
| Total non-interest-bearing liabilities as at 31.12.2016 |
78,625,428 |
3,058,595 |
1,529,112 |
309,278 |
80,990,275 |
|
164,512,688 |
| Total liabilities and equity – as at 31.12.2017 |
606,966,878 |
322,500,819 |
43,035,424 |
32,755,419 |
150,562,116 |
1,155,820,656 |
|
| Total liabilities and equity – as at 31.12.2016 |
584,796,723 |
267,580,273 |
34,355,624 |
23,452,761 |
110,798,193 |
|
1,020,983,574 |
| Percentage – as at 31.12.2017(*) |
52.52 |
27.90 |
3.72 |
2.83 |
13.03 |
100.00 |
|
| Percentage – as at 31.12.2016(*) |
57.28 |
26.21 |
3.36 |
2.30 |
10.85 |
|
100.00 |
(*) Total liabilities and shareholders’ funds of each maturity bucket as a percentage of total liabilities and shareholders’ funds employed by the Group.
Bank
Maturity analysis of the assets and liabilities of the Bank is given in Note 69.2.2 on “Financial Risk Review”.
63. Operating Segments
An operating segment is a component of the Group that engages in business activities from which it may earn revenues and incur expenses, including revenues and expenses that relate to transactions with any of the Group’s other components, whose operating results are reviewed regularly by the Corporate Management Team headed by the Managing Director/Chief Executive Officer (being the chief operating decision-maker) to make decisions about resources allocated to each segment and assess its performance, and for which discrete financial information is available.
The Group has five strategic divisions which are reportable segments, namely:
| Operating segment |
|
Types of products and services offered |
| Personal banking |
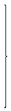 |
Refer section on Key Business Lines Review under Capital Management for details on product portfolio by Business Lines |
| Corporate banking |
| International operations |
| Investment banking |
| Dealing and treasury |
Segment performance is evaluated based on operating profits or losses which, in certain respects, are measured differently from operating profits or losses in the Consolidated Financial Statements. Income taxes are managed on a Group basis and are not allocated to operating segments.
The following table presents the income, profit, asset and liability information on the Group’s strategic business divisions for the year ended December 31, 2017 and comparative figures for the year ended December 31, 2016.
|
Personal banking |
Corporate banking |
International operations |
Investment banking |
Dealing/treasury |
Unallocated/eliminations |
Total/consolidated |
| For the year ended |
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
| December 31, |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| External operating income: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Net interest income |
26,884,392 |
23,255,124 |
4,639,252 |
4,528,344 |
4,044,558 |
3,214,891 |
381,502 |
1,026,278 |
1,559,382 |
(125,417) |
2,058,212 |
1,229,056 |
39,567,298 |
33,128,276 |
Foreign exchange
profit |
217,330 |
198,679 |
699,565 |
822,894 |
1,015,851 |
509,081 |
– |
– |
(1,335,721) |
795,504 |
– |
– |
597,025 |
2,326,158 |
Net fee and
commission
income |
6,135,191 |
4,857,448 |
1,803,963 |
1,594,813 |
934,398 |
609,430 |
45,242 |
23,505 |
5,672 |
3,981 |
– |
– |
8,924,466 |
7,089,177 |
| Other income |
454,232 |
779,594 |
334,100 |
353,668 |
125,674 |
190,003 |
42,303 |
8,984 |
213,662 |
64,252 |
514,857 |
458,138 |
1,684,828 |
1,854,639 |
| Total operating income |
33,691,145 |
29,090,845 |
7,476,880 |
7,299,719 |
6,120,481 |
4,523,405 |
469,047 |
1,058,767 |
442,995 |
738,320 |
2,573,069 |
1,687,194 |
50,773,617 |
44,398,250 |
| Impairment loss expenses |
(2,471,052) |
202,442 |
564,494 |
(1,726,375) |
(319,356) |
(59,393) |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
(2,225,914) |
(1,583,326) |
| Net operating income |
31,220,093 |
29,293,287 |
8,041,374 |
5,573,344 |
5,801,125 |
4,464,012 |
469,047 |
1,058,767 |
442,995 |
738,320 |
2,573,069 |
1,687,194 |
48,547,703 |
42,814,924 |
| Segment result |
16,281,986 |
14,328,813 |
5,414,227 |
4,874,706 |
4,086,117 |
3,148,044 |
287,326 |
625,923 |
126,225 |
(4,086) |
(2,919,235) |
(2,865,270) |
23,276,646 |
20,108,130 |
| Profit from operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23,276,646 |
20,108,130 |
| Share of profit of associates – net of tax |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3,678 |
6,454 |
| Income tax expense |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(6,653,817) |
(5,648,160) |
| Non-controlling interest |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(20,544) |
43,909 |
| Net profit for the year, attributable to equity holders of the parent
| |
|
|
|
|
|
16,605,963 |
14,510,333 |
|
Personal banking |
Corporate banking |
International operations |
Investment banking |
Dealing/treasury |
Unallocated/eliminations |
Total/consolidated |
| As at |
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
| December 31, |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Other information |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
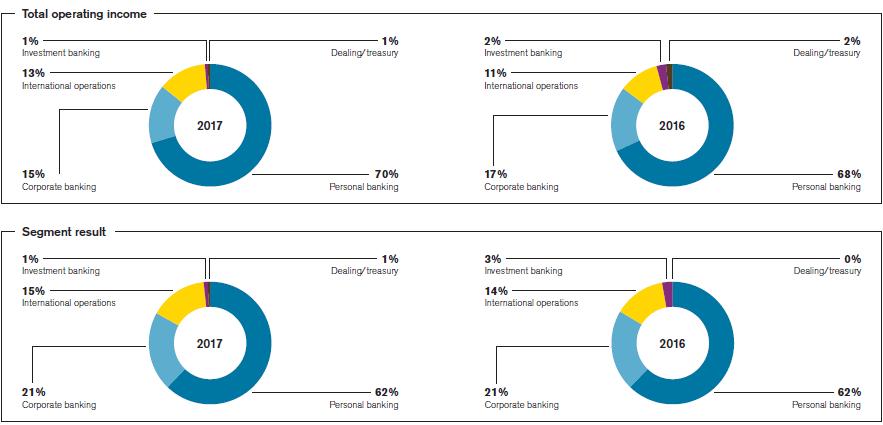
Segment
assets |
443,643,154 |
340,853,854 |
240,649,838 |
229,759,156 |
128,456,896 |
112,387,766 |
17,270,623 |
19,644,842 |
262,780,975 |
257,143,130 |
62,909,326 |
61,085,967 |
1,155,710,812 |
1,020,874,715 |
Investment in
associates |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
109,844 |
108,859 |
109,844 |
108,859 |
Unallocated
assets |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Total assets |
443,643,154 |
340,853,854 |
240,649,838 |
229,759,156 |
128,456,896 |
112,387,766 |
17,270,623 |
19,644,842 |
262,780,975 |
257,143,130 |
63,019,170 |
61,194,826 |
1,155,820,656 |
1,020,983,574 |
Segment
liabilities |
690,860,560 |
601,064,166 |
151,728,410 |
145,104,008 |
103,813,211 |
86,181,038 |
17,380,467 |
12,444,122 |
75,403,237 |
92,910,135 |
7,768,065 |
3,464,682 |
1,046,953,950 |
941,168,151 |
Unallocated
liabilities |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Total liabilities |
690,860,560 |
601,064,166 |
151,728,410 |
145,104,008 |
103,813,211 |
86,181,038 |
17,380,467 |
12,444,122 |
75,403,237 |
92,910,135 |
7,768,065 |
3,464,682 |
1,046,953,950 |
941,168,151 |
|
Personal banking |
Corporate banking |
International operations |
Investment banking |
Dealing/treasury |
Unallocated/eliminations |
Total/consolidated |
| For the year ended |
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
| Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Information on
cash flows |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash flows
from operating
activities |
3,977,097 |
48,260,328 |
(7,219,784) |
(20,442,140) |
322,609 |
(491,909) |
140,802 |
(40,710) |
(191,366) |
(21,391,095) |
– |
– |
(2,970,642) |
5,894,474 |
Cash flows
from investing
activities |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
3,362,948 |
1,124,546 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
3,362,948 |
1,124,546 |
Cash flows
from financing
activities |
(2,274,217) |
(1,298,062) |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
(88,053) |
12,191,770 |
6,177,191 |
(3,204,500) |
3,814,921 |
7,689,208 |
| Capital expenditure |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Property, plant and equipment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(2,105,701) |
(1,468,902) |
| Intangible assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(352,329) |
(422,175) |
| Net cash flow generated during the year |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,749,197 |
12,817,151 |
64. Related Party Disclosures
The Bank carried out transactions in the ordinary course of business on an arm’s length basis at commercial rates with parties who are defined as Related Parties as per the Sri Lanka Accounting Standard – LKAS 24 – “Related Party Disclosures”, other than, transactions that the Key Management Personnel (KMP) have availed under schemes uniformly applicable to all staff at concessionary rates.
64.1 Parent and ultimate controlling party
The Bank does not have an identifiable parent of its own.
64.2 Key Management Personnel (KMP)
KMP are those persons having authority and responsibility for planning, directing and controlling the activities of the entity directly
or indirectly.
KMP of the Bank
The Board of Directors of the Bank has been classified as KMP of the Bank.
KMP of the Group
As the Bank is the ultimate parent of the subsidiaries listed out in Note 1.3 to the Financial Statements, the Board of Directors of the Bank has the authority and responsibility for planning, directing and controlling the activities of the Group directly or indirectly. Accordingly, the Board of Directors of the Bank is also KMP of the Group. Therefore, officers who are only Directors of the subsidiaries and not of the Bank have been classified as KMP only for that respective subsidiary.
64.2.1 Transactions with KMP
64.2.1.1 Compensation of KMP – Bank
| For the year ended December 31, |
2017 |
2016 |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Short-term employment benefits |
159,190 |
124,478 |
| Post-employment benefits |
7,831 |
6,984 |
| Total |
167,021 |
131,462 |
64.2.1.2 Compensation of KMP – Group
| For the year ended December 31, |
2017 |
2016 |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Short-term employment benefits |
161,282 |
125,648 |
| Post-employment benefits |
7,831 |
6,984 |
| Total |
169,113 |
132,632 |
64.2.2 Transactions, arrangements and agreements involving KMP and their Close Family Members (CFM)
CFM of a KMP are those family members who may be expected to influence, or be influenced by, that KMP in their dealings with the entity. They may include KMP’s domestic partner and children, children of the KMP’s domestic partner and dependants of the KMP or the KMP’s domestic partner. CFM are related parties to the Group/Bank.
64.2.2.1 Statement of Financial Position – Bank
|
Year-end balance |
Average balance |
| As at December 31, |
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Assets |
|
|
|
|
| Loans and advances |
18,890 |
10,229 |
9,282 |
9,462 |
| Credit cards |
115 |
– |
427 |
238 |
| Total |
19,005 |
10,229 |
9,709 |
9,700 |
|
|
|
|
|
| Liabilities |
|
|
|
|
| Deposits |
228,579 |
145,701 |
167,137 |
79,474 |
| Securities sold under repurchase agreements |
7,844 |
35,062 |
30,123 |
31,198 |
| Debentures |
2,000 |
2,000 |
2,000 |
355 |
| Total |
238,423 |
182,763 |
199,260 |
111,027 |
64.2.2.2 Commitments and contingencies – Bank
|
Year-end balance |
Average balance |
| As at December 31, |
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Undrawn facilities |
18,035 |
10,380 |
13,024 |
11,716 |
| Total |
18,035 |
10,380 |
13,024 |
11,716 |
64.2.2.3 Direct and indirect accommodation – Bank
|
Year-end balance |
| As at December 31, |
2017 |
2016 |
|
% |
% |
| Direct and indirect accommodation as a % of the Bank’s Regulatory Capital |
0.03 |
0.02 |
No impairment losses have been recorded against balances outstanding with KMP and CFM.
64.2.2.4 Income Statement
| For the Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
2017 |
2016 |
|
Note |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Interest income |
|
|
777 |
626 |
| Interest expense |
|
|
17,226 |
7,747 |
| Other income |
|
|
– |
20 |
| Compensation to KMP |
64.2.1.1 & 64.2.1.2 |
|
167,021 |
131,462 |
64.2.2.5 Share-based transactions of KMP and CFM
| As at the year end |
2017 |
2016 |
| Number of ordinary shares held |
1,206,569 |
810,939 |
| Dividends paid (in Rs. ’000) |
6,304 |
4,762 |
| Number of cumulative exercisable options under the Employee Share Option Plan (ESOP) 2008 |
|
|
| Tranche II |
50,270 |
98,678 |
| Tranche III |
105,695 |
155,603 |
| Number of cumulative exercisable options under the Employee Share Option Plan (ESOP) 2015 |
|
|
| Tranche I |
83,416 |
81,869 |
| Tranche II |
85,912 |
– |
64.2.3 Transactions, arrangements and agreements involving entities which are controlled, and/or significantly influenced by the KMP or their CFM
64.2.3.1 Statement of Financial Position
|
Year-end balance |
Average balance |
|
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Assets |
|
|
|
|
| Loans and advances |
3,693,085 |
266,349 |
2,220,358 |
80,967 |
| Credit cards |
777 |
– |
596 |
– |
| Total |
3,693,862 |
266,349 |
2,220,954 |
80,967 |
|
|
|
|
|
| Liabilities |
|
|
|
|
| Deposits |
1,305,617 |
977,122 |
986,253 |
276,411 |
| Securities sold under repurchase agreements |
119,000 |
126,237 |
74,093 |
426 |
| Debentures |
24,310 |
24,310 |
24,310 |
4,317 |
| Total |
1,448,927 |
1,127,669 |
1,084,656 |
281,154 |
64.2.3.2 Commitments and contingencies
|
Year-end balance |
Average balance |
|
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Guarantees |
76,530 |
71,280 |
74,055 |
71,280 |
| Undrawn facilities |
354,901 |
379,266 |
218,930 |
279,891 |
| Total |
431,431 |
450,546 |
292,985 |
351,171 |
64.2.3.3 Direct and indirect accommodation
|
|
Year-end balance |
|
|
2017 |
2016 |
|
|
% |
% |
| Direct and indirect accommodation as a % of the Bank’s Regulatory Capital |
|
3.37 |
0.69 |
64.2.3.4 Income Statement
| For the year ended December 31, |
2017 |
2016 |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Interest income |
233,786 |
10,451 |
| Interest expense |
39,411 |
9,916 |
| Other income |
118 |
– |
64.3 Transactions with group entities
The Group entities include the subsidiaries and the associates of the Bank.
64.3.1 Transactions with subsidiaries
64.3.1.1 Statement of Financial Position
|
Year-end balance |
Average balance |
|
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Assets |
|
|
|
|
| Loans and advances |
841,060 |
786,000 |
879,790 |
564,749 |
| Lease receivables |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Other receivables |
31,439 |
92,857 |
62,148 |
91,727 |
| Impairment for other receivables |
– |
(55,684) |
– |
(54,554) |
| Total |
872,499 |
823,173 |
941,938 |
601,922 |
|
|
|
|
|
| Liabilities |
|
|
|
|
| Deposits |
502,575 |
178,827 |
120,953 |
108,269 |
| Securities sold under repurchase agreements |
142,550 |
238,508 |
202,877 |
145,944 |
| Other |
74,523 |
20,061 |
47,292 |
23,137 |
| Total |
719,648 |
437,396 |
371,122 |
277,350 |
64.3.1.2 Commitments and contingencies
|
Year-end balance |
Average balance |
|
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Letters of credit |
– |
– |
– |
1,126 |
| Undrawn facilities |
100,000 |
62,565 |
84,881 |
113,165 |
| Total |
100,000 |
62,565 |
84,881 |
114,291 |
64.3.1.3 Direct and indirect accommodation
|
|
Year-end balance |
|
|
2017 |
2016 |
|
|
% |
% |
| Direct and indirect accommodation as a % of the Bank’s Regulatory Capital |
|
0.79 |
0.72 |
64.3.1.4 Income Statement
| For the Year Ended December 31, |
2017 |
2016 |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Interest income |
143,796 |
58,002 |
| Interest expense |
32,695 |
26,731 |
| Other income |
182,826 |
103,569 |
| Impairment charges |
– |
3,306 |
| Expenses |
523,214 |
454,126 |
64.3.1.5 Other transactions
| For the year ended December 31, |
2017 |
2016 |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Payments made to OneZero Company Ltd. in relation to purchase of computer hardware and software |
29,738 |
8,253 |
64.3.2 Transactions with associates
64.3.2.1 Statement of Financial Position
|
Year-end balance |
Average balance |
|
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Assets |
|
|
|
|
| Loans and advances |
– |
– |
32 |
29 |
| Lease receivables |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Total |
– |
– |
32 |
29 |
|
|
|
|
|
| Liabilities |
|
|
|
|
| Deposits |
35,468 |
48,606 |
19,945 |
38,967 |
| Securities sold under repurchase agreements |
– |
– |
16,228 |
– |
| Total |
35,468 |
48,606 |
36,173 |
38,967 |
64.3.2.2 Commitments and contingencies
|
Year-end balance |
Average balance |
|
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Undrawn facilities |
1,000 |
– |
– |
– |
| Total |
1,000 |
– |
– |
– |
64.3.2.3 Direct and indirect accommodation
|
Year end Balance |
|
2017 |
2016 |
|
% |
% |
| Direct and indirect accommodation as a % of the Bank’s Regulatory Capital |
0.00 |
0.00 |
64.3.2.4 Income Statement
| For the year ended December 31, |
2017 |
2016 |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Interest income |
8 |
7 |
| Interest expense |
3,666 |
3,310 |
| Other income |
21,213 |
22,698 |
| Expenses |
71,194 |
– |
64.3.2.5 Other transactions
|
2017 |
2016 |
| Number of ordinary shares of the Bank held by the associates as at the year-end |
46,154 |
4,605 |
| Dividend paid (Rs. ’000) |
278 |
29 |
64.4 Transactions with other related entities
Other related entities include significant investors (either entities or individuals) that have control, joint control or significant influence,
post-employment benefit plans for the Bank’s employees.
64.4.1 Transactions with the post-employment benefit plans for the employees of the Bank
64.4.1.1 Statement of Financial Position
|
Year-end balance |
Average balance |
|
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Assets |
|
|
|
|
| Loans and advances |
– |
– |
474 |
– |
| Total |
– |
– |
474 |
– |
|
|
|
|
|
| Liabilities |
|
|
|
|
| Deposits |
9,427,494 |
12,681,135 |
8,452,541 |
7,615,681 |
| Securities sold under repurchase agreements |
– |
386,447 |
83,265 |
293,317 |
| Total |
9,427,494 |
13,067,582 |
8,535,806 |
7,908,998 |
64.4.1.2 Income Statement
| For the year ended December 31, |
2017 |
2016 |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Interest income |
114 |
30 |
| Interest expense |
1,075,241 |
821,179 |
| Contribution made/taxes paid by the Bank |
1,005,342 |
1,007,451 |
65. Non-Cash Items Included in Profit Before Tax
|
GROUP |
BANK |
| As at December 31, |
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Depreciation of property, plant and equipment |
1,185,698 |
1,093,088 |
1,097,096 |
1,022,648 |
| Amortisation of leasehold property |
1,452 |
1,452 |
942 |
942 |
| Amortisation of intangible assets |
229,764 |
173,790 |
209,766 |
165,903 |
| Impairment losses on loans and advances |
2,225,914 |
1,583,326 |
1,956,725 |
1,511,158 |
| Other impairment |
– |
– |
(42,484) |
18,656 |
| Contributions to defined benefit plans – Unfunded schemes |
288,791 |
234,262 |
279,249 |
227,816 |
| Provision made o/a of leave encashment |
79,128 |
76,193 |
79,128 |
76,193 |
| Equity-settled Share-based payments |
138,341 |
206,174 |
138,341 |
206,174 |
| Unamortised interest payable o/a subodinated liabilities |
12,211 |
12,210 |
12,211 |
12,210 |
| Mark to market on other financial instruments – held for trading |
(85,627) |
129,562 |
(85,627) |
129,562 |
| Loss on write-off intangible assets |
7,241 |
303 |
– |
303 |
| Effect of exchange rate variances on investment in subsidiaries |
– |
– |
(26,349) |
(30,136) |
| Effect of exchange rate variances on loans and receivables to banks |
(16,054) |
(23,352) |
(16,054) |
(23,352) |
| Effect of exchange rate variances on property, plant and equipment |
(168) |
(2,024) |
882 |
(2,012) |
| Effect of exchange rate variances on intangible assets |
(3,208) |
(553) |
429 |
(540) |
| Effect of exchange rate variances on defined benefit plans |
(7,279) |
7,782 |
(7,279) |
7,782 |
| Effect of exchange rate variances on subordinated liabilities |
288,750 |
420,000 |
288,750 |
420,000 |
| Net effect of exchange rate variances on net deferred tax liability |
995 |
(4,980) |
4,626 |
(4,979) |
| Net effect of exchange rate variances on income tax liability |
(45,703) |
56,937 |
(45,820) |
56,937 |
| Grossed up notional tax and withholding tax credits |
(1,985,107) |
(1,209,319) |
(1,961,769) |
(1,206,343) |
| Total |
2,315,139 |
2,754,851 |
1,882,763 |
2,588,922 |
66. Change in Operating Assets
|
GROUP |
BANK |
| As at December 31, |
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Net (increase)/decrease in derivative financial instruments |
(1,281,707) |
3,065,340 |
(1,281,707) |
3,065,340 |
| Net (increase)/decrease in balances with central banks |
(1,611,091) |
(15,714,241) |
(928,241) |
(15,652,188) |
| Net (increase)/decrease in placements with banks |
(5,914,770) |
5,475,040 |
(5,914,770) |
5,475,040 |
| Net (increase)/decrease in securities purchased under resale agreements |
– |
8,002,100 |
– |
8,002,100 |
| Net (increase)/decrease in other financial assets – Held for trading |
683,448 |
2,556,114 |
683,448 |
2,556,114 |
| Net (increase)/decrease in loans and receivables to customers |
(124,540,556) |
(111,789,686) |
(123,385,064) |
(109,414,259) |
| Net (increase)/decrease in financial investments – Available for sale |
12,820,870 |
39,672,872 |
12,951,296 |
39,724,256 |
| Financial investments – Held-to-maturity |
(5,739,198) |
(63,626,598) |
(2,581,454) |
(60,981,298) |
| Net (increase)/decrease in financial investments – Loans and receivables |
(263,047) |
4,815,666 |
(263,047) |
4,815,666 |
| Net (increase)/decrease in other assets |
(880,418) |
(4,385,542) |
(859,996) |
(4,346,881) |
| Total |
(126,726,469) |
(131,928,935) |
(121,579,535) |
(126,756,110) |
67. Change in Operating Liabilities
|
GROUP |
BANK |
| As at December 31, |
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Net increase/(decrease) in due to banks |
(10,853,499) |
39,308,995 |
(10,487,820) |
37,289,692 |
| Net increase/(decrease) in derivative financial instruments |
2,158,997 |
(375,735) |
2,158,997 |
(375,735) |
| Net increase/(decrease) in securities sold under repurchase agreements |
(20,096,576) |
(42,620,742) |
(20,190,702) |
(42,517,343) |
| Net increase/(decrease) in deposits from banks, customers and debt securities issued |
113,959,368 |
119,289,396 |
110,564,017 |
115,461,684 |
| Net increase/(decrease) in other borrowings |
14,515,940 |
(715,483) |
14,515,940 |
(715,483) |
| Net increase/(decrease) in other provisions |
(1,874) |
– |
(1,874) |
– |
| Net increase/(decrease) in other liabilities |
583,523 |
2,236,019 |
633,847 |
2,122,523 |
| Net increase/(decrease) in due to subsidiaries |
– |
– |
54,462 |
(6,151) |
| Total |
100,265,879 |
117,122,450 |
97,246,867 |
111,259,187 |
68. Operating Leases
68.1 Operating lease commitments (payables)
A number of branches and office premises occupied by the Group are under operating leases. These leases have an average life of three to six years. Lease agreements include clauses to enable upward revision of the rental payments on a periodic basis to reflect market conditions. There are no restrictions placed upon the Group by entering into these leases.
Future minimum rentals payable under non-cancellable operating leases are as follows:
|
GROUP |
BANK |
| As at December 31, |
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Less than one year |
937,070 |
760,677 |
890,519 |
707,066 |
| Between one to five years |
2,510,540 |
1,889,163 |
2,352,812 |
1,762,161 |
| Over five years |
2,186,383 |
1,066,952 |
2,076,645 |
927,007 |
| Total |
5,633,993 |
3,716,792 |
5,319,976 |
3,396,234 |
68.2 Operating lease commitments (receivables)
The Group has entered into operating leases to rent its own properties (mainly consisting of areas not currently occupied by the branches). Lease agreements include clauses to enable upward revision of rental income on a periodic basis to reflect market conditions. These leases have an average life of three to five years. There are no restrictions placed upon the Group by entering into these leases.
Future minimum rentals receivable under non-cancellable operating leases are as follows:
|
GROUP |
BANK |
| As at December 31, |
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Less than one year |
6,007 |
6,042 |
1,820 |
3,218 |
| Between one to five years |
10,289 |
12,167 |
2,440 |
3,469 |
| Over five years |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Total |
16,296 |
18,209 |
4,260 |
6,687 |
69. Financial Risk Review
This note presents information about the Bank’s exposure to financial risks and the Bank’s management of capital.
| For information on the Bank’s Financial Risk Management Framework |
|
|
Introduction |
|
| 69.1 |
Credit risk |
|
| 69.1.1 |
Credit quality analysis |
|
| 69.1.2 |
Impaired loans and receivables and investment in debt securities |
|
| 69.1.3 |
Collaterals held |
|
| 69.1.4 |
Concentration of credit risk |
|
| 69.1.5 |
Exposures to unrated countries |
|
| 69.2 |
Liquidity risk |
|
| 69.2.1 |
Exposure to liquidity risk |
|
| 69.2.2 |
Maturity analysis of financial assets and financial liabilities |
|
| 69.2.3 |
Liquidity reserves |
|
| 69.2.4 |
Financial assets available to support future funding |
|
| 69.3 |
Market risk |
|
| 69.3.1 |
Exposure to market risk – Trading and non-trading portfolios |
|
| 69.3.2 |
Exposure to interest rate risk – Sensitivity analysis |
|
| 69.3.3 |
Exposure to currency risk – Non-trading portfolio |
|
| 69.3.4 |
Exposure to equity price risk |
|
| 69.4 |
Operational risk |
|
| 69.5 |
Capital management and Pillar III disclosures as per Basel III |
|
| 69.5.1 |
Regulatory capital |
|
| 69.5.2 |
Capital allocation |
|
| 69.5.3 |
Pillar III disclosures as per Basel III |
|
Introduction
As a financial intermediary, the Bank is exposed to various types of risks including credit, market, liquidity and operational risks which are inherent in the Bank’s activities. Managing these risks is critical for the sustainability of the Bank and plays a pivotal role in all activities of the Bank. Risk Management function strives to identify potential risks in advance, analyse them and take precautionary steps to mitigate the impact of risk whilst optimising through risk adjusted returns within the risk appetite of the Bank.
Risk Management framework
The overall responsibility and oversight of the Risk Management framework of the Bank is vested with the Board of Directors (BOD). The Board Integrated Risk Management Committee (BIRMC), a mandatory Subcommittee set up by the Board, in turn is entrusted with the development of the Bank’s Risk Management Policies and monitoring of due compliance of same through the Executive Integrated Risk Management Committee (EIRMC).
The Risk Management Policies spell out the risk appetite of the Bank and has incorporated risk exposure limits and controls to monitor adherence to the limits in force. These Policies and Systems are reviewed regularly to reflect the changing market conditions and the products and services offered.
The Bank strives to inculcate a Risk Management Culture through continuous training, work ethics and standards.
Refer Note 3 to the Financial Statements for more information on the Risk Management Framework of the Bank.
Integrated Risk Management Department (IRMD)
Business Units are the Risk Owners and have the primary responsibility for Risk Management. The IRMD acts as the second line of defence in managing the Risk. The IRMD through Chief Risk Officer reports to the BIRMC thus ensuring its independence.
Risk measurement and reporting
The Bank uses robust risk measurement techniques based on the type of risk and industry best practices. The Bank also carries out Stress Testing which is a key aspect of the Internal Capital Adequacy Assessment Process ( ICAAP ) and the Risk Management Framework provides an insight on the impact of extreme, but plausible scenarios on the Bank’s risk profile. The results are reported to the EIRMC and to the BIRMC on a periodic basis.
The Bank establishes policies, limits and thresholds within the Risk appetite. These limits reflect the business strategy and market environment of the Bank as well as the level of risk that the Bank is willing to accept (risk appetite). The monitoring and control mechanism therefore, is based on risk appetite of the Bank.
69.1 Credit risk
The financial loss resulting from a borrower or counterparty to a financial instrument failing or delaying to meet its contractual obligations is referred to as credit risk. It arises principally from the loans and receivables to banks and other customers and investments in debt securities. In addition to the credit risk from direct funding exposure i.e., On-Balance Sheet exposure, indirect liabilities such as Letters of Credit, Guarantees etc. also would expose the Bank to credit risk.
The Bank considers and consolidates all elements of credit risk exposure (such as individual obligour default risk, country and sector concentration risks) to ensure stringent Credit Risk Management.
69.1.1 Credit quality analysis
69.1.1 (a) Maximum exposure to credit risk by risk rating
|
|
|
Loans and receivables to
other customers |
Loans and receivables
to banks |
Financial investments |
Lending commitments and
contingencies |
| As at December 31, |
|
|
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
|
Notes |
Page No. |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Maximum exposure to credit risk |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Carrying amount |
31-36 |
|
737,446,567 |
616,018,228 |
640,512 |
624,458 |
271,400,274 |
277,816,593 |
|
|
| Amount committed/contingencies |
59 |
285 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
563,048,700 |
497,235,276 |
At amortised cost –
Loans and receivables |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Government securities
(Risk free investments) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
40,566,702 |
40,076,392 |
|
|
| Rating 0-4: Investment grade(*) |
|
|
476,843,647 |
382,276,912 |
– |
– |
8,145,775 |
11,747,634 |
|
|
| Rating 5-6: Moderate risk |
|
|
249,066,153 |
222,439,065 |
640,512 |
624,458 |
|
|
|
|
| Rating S: High risk |
|
|
2,035,633 |
1,696,932 |
– |
– |
|
|
|
|
| Rating 7-9: Extreme risk |
|
|
26,762,544 |
26,977,998 |
– |
– |
|
|
|
|
| Gross carrying amount |
|
|
754,707,977 |
633,390,907 |
640,512 |
624,458 |
48,712,477 |
51,824,026 |
– |
– |
Less: Provision for impairment
(Individual and collective) |
|
|
17,261,410 |
17,372,679 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Net carrying amount |
|
|
737,446,567 |
616,018,228 |
640,512 |
624,458 |
48,712,477 |
51,824,026 |
– |
– |
| Financial investments –
Available for sale |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Government securities
(Risk free investments) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
154,167,169 |
159,573,316 |
|
|
Rating 0-4: Investment
grade |
|
|
|
|
|
|
546,963 |
450,155 |
|
|
| Rating 5-6: Moderate risk |
|
|
|
|
|
|
– |
– |
|
|
| Rating S: High risk |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Rating 7-9: Extreme risk |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Gross/net carrying amount |
34 |
232 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
154,714,132 |
160,023,471 |
– |
– |
| Financial investments – Held to maturity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Government securities
(Risk free investments) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
53,555,302 |
50,980,717 |
|
|
Rating 0-4: Investment
grade |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Rating 5-6: Moderate risk |
|
|
|
|
|
|
10,007,450 |
10,000,581 |
|
|
| Rating S : High risk |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Rating 7-9: Extreme risk |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Gross/net carrying amount |
35 |
238 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
63,562,752 |
60,981,298 |
– |
– |
| Other financial instruments – Held for trading |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Government securities
(Risk free investments) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2,357,876 |
3,505,335 |
|
|
Rating 0-4: Investment
grade |
|
|
|
|
|
|
314,745 |
293,809 |
|
|
| Rating 5-6: Moderate risk |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,738,292 |
1,188,654 |
|
|
| Rating S: High risk |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Rating 7-9: Extreme risk |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Gross/net carrying amount |
31 |
222 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
4,410,913 |
4,987,798 |
– |
– |
| Total net carrying amount |
|
|
737,446,567 |
616,018,228 |
640,512 |
624,458 |
271,400,274 |
277,816,593 |
– |
– |
| Off-Balance Sheet(**) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Maximum exposure |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Lending commitments |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Grade 0-6: Investment
grade to moderate risk |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
124,594,675 |
131,381,356 |
| Contingencies |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Grade 0-6: Investment
grade to moderate risk |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
438,454,025 |
365,853,920 |
| Total exposure |
59 |
285 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
563,048,700 |
497,235,276 |
(*) Investment grade also includes cash, gold.
(**) Amounts reported above does not include capital commitments disclosed in Note 59 on “Contingent Liabilities and Commitments” .
69.1.1 (b) Age analysis by class of financial assets
The maximum exposure to credit risk for class of financial assets by risk rating and by age are given below:
|
Loans and receivables to
other customers |
Loans and receivables
to banks |
Financial investments |
Lending commitments and contingencies |
| As at December 31, |
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
2017 |
2016 |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Government securities
(Risk free investments) |
– |
– |
|
|
250,647,049 |
254,135,760 |
|
|
| Gross carrying amount |
– |
– |
– |
– |
250,647,049 |
254,135,760 |
– |
– |
| Neither past due nor individually impaired |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Rating 0-4: Investment grade |
472,230,045 |
377,513,301 |
|
|
9,007,483 |
12,491,598 |
282,344,809 |
268,186,647 |
| Rating 5-6: Moderate risk |
244,352,749 |
218,392,511 |
640,512 |
624,458 |
11,745,742 |
11,189,235 |
280,703,891 |
229,048,629 |
| Gross carrying amount |
716,582,794 |
595,905,812 |
640,512 |
624,458 |
20,753,225 |
23,680,833 |
563,048,700 |
497,235,276 |
| Past due but not individually Impaired |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Less than 3 months |
8,160,289 |
8,484,516 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 3 to 6 months |
856,410 |
507,450 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 6 to 12 months |
724,801 |
859,216 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 12 to 18 months |
469,520 |
490,692 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| More than 18 months |
4,870,915 |
5,041,144 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Gross carrying amount |
15,081,935 |
15,383,018 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Individually impaired |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Less than 3 months |
12,533,705 |
11,145,557 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 3 to 6 months |
1,292,185 |
748,471 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 6 to 12 months |
404,605 |
598,082 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 12 to 18 months |
1,209,297 |
893,546 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| More than 18 months |
7,603,456 |
8,716,421 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Gross carrying amount |
23,043,248 |
22,102,077 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Total gross carrying amount |
754,707,977 |
633,390,907 |
640,512 |
624,458 |
271,400,274 |
277,816,593 |
563,048,700 |
497,235,276 |
| Less: Provision for impairment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Individual |
7,853,654 |
8,453,457 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Collective |
9,407,756 |
8,919,222 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Total provision for impairment |
17,261,410 |
17,372,679 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Total net carrying amount |
737,446,567 |
616,018,228 |
640,512 |
624,458 |
271,400,274 |
277,816,593 |
563,048,700 |
497,235,276 |
The methodology of the impairment assessment is explained in Note 18.
69.1.1 (c) Credit risk exposure for each internal credit rating on facilities and probability of historical default rates
Through adoption of a robust risk grading system that falls in line with Basel requirements, the Bank maintains accurate and consistent risk ratings across the credit portfolio in accordance with the established policy framework to ensure the quality of its credit portfolio. The risk grading framework consists of several ratings of risks to represent varying degrees of risks as an indicator for Lending Officers to evaluate the overall risk profile of counterpart and to arrive at an acceptable risk return trade-off. It also provides a tool for the Management to assess the credit exposures across all lines of business, geographic regions and products. The risk gradings of the borrowers are reviewed at least annually or more frequently in a deteriorating risk profile of the counterparties.
The Bank’s internal credit rating of the loans and receivable portfolio together with historical default rates and respective gross carrying amounts are given in the table below:
| As at December 31, |
|
|
2017 |
2016 |
| Bank’s Internal Credit Rating |
Note |
|
Probability of
historical default
rates |
Gross carrying
amount |
Probability of
historical default
rates |
Gross carrying
amount |
|
|
|
% |
Rs. ’000 |
% |
Rs. ’000 |
| Gold |
|
|
9.50 |
1,337,133 |
10.34 |
1,246,374 |
| Investment grade |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Rating – 0 |
|
|
0.10 |
100,062,702 |
0.21 |
74,103,326 |
| Rating – 1 |
|
|
0.19 |
11,494,072 |
0.17 |
8,137,933 |
| Rating – 2 |
|
|
0.22 |
39,968,653 |
0.22 |
32,231,244 |
| Rating – 3 |
|
|
0.35 |
145,571,878 |
0.42 |
124,005,233 |
| Rating – 4 |
|
|
0.55 |
173,795,607 |
0.60 |
137,789,192 |
| Subtotal |
|
|
|
472,230,045 |
|
377,513,302 |
| Moderate risk |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Rating – 5 |
|
|
0.68 |
207,167,645 |
0.75 |
183,723,935 |
| Rating – 6 |
|
|
0.98 |
37,185,104 |
1.31 |
34,668,576 |
| Subtotal |
|
|
|
244,352,749 |
|
218,392,511 |
| Past due but not individually impaired |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| High risk |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Rating – S |
|
|
21.51 |
1,272,065 |
23.57 |
1,081,476 |
| Extreme risk |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Rating – 7 |
|
|
47.52 |
6,804,251 |
54.78 |
7,474,654 |
| Rating – 8 |
|
|
68.45 |
1,042,713 |
71.22 |
630,680 |
| Rating – 9 |
|
|
100.00 |
5,962,906 |
100.00 |
6,196,207 |
| Subtotal |
|
|
|
15,081,935 |
|
15,383,017 |
| Impaired |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Individually Impaired(*) |
|
|
– |
23,043,248 |
– |
22,102,077 |
| Total |
33 |
|
|
754,707,977 |
|
633,390,907 |
(*) Probability of historical default rates are not calculated for individually impaired loans and receivables.
69.1.1 (d) Credit quality by class of financial assets
The table below shows the credit quality by the class of asset for all financial assets exposed to credit risk, based on the Bank’s internal
credit rating:
| As at December 31, 2017 |
|
|
Neither past due nor individually impaired |
|
|
|
|
Note |
|
Government
guarantee |
Investment
grade |
Moderate risk |
Past due but not
individually
impaired |
Individually
impaired |
Total |
|
|
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Cash and cash equivalents |
27 |
|
– |
33,224,619 |
– |
– |
– |
33,224,619 |
| Balances with central banks |
28 |
|
44,801,446 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
44,801,446 |
| Placements with banks |
29 |
|
– |
17,633,269 |
– |
– |
– |
17,633,269 |
Securities purchased under
resale agreements |
|
|
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Derivative financial assets |
30 |
|
– |
2,334,536 |
– |
– |
– |
2,334,536 |
Other financial instruments –
Held for trading |
31 |
|
2,357,876 |
314,745 |
1,738,292 |
– |
– |
4,410,913 |
Loans and receivables
to banks |
32 |
|
|
– |
640,512 |
|
|
640,512 |
Loans and receivables to
other customers |
33 |
|
– |
469,669,456 |
242,786,716 |
9,800,801 |
15,189,594 |
737,446,567 |
| Corporate banking |
|
|
– |
249,817,145 |
86,639,832 |
5,776,899 |
3,931,899 |
346,165,775 |
| Amortised cost |
|
|
– |
251,613,579 |
87,342,167 |
6,116,798 |
6,517,529 |
351,590,073 |
Less – Provision for
impairment |
|
|
– |
1,796,434 |
702,335 |
339,899 |
2,585,630 |
5,424,298 |
| Personal banking |
|
|
– |
219,852,311 |
156,146,884 |
4,023,902 |
11,257,695 |
391,280,792 |
| Amortised cost |
|
|
– |
220,616,463 |
157,010,582 |
8,965,140 |
16,525,719 |
403,117,904 |
Less – Provision for
impairment |
|
|
– |
764,152 |
863,698 |
4,941,238 |
5,268,024 |
11,837,112 |
Financial investments –
Available for sale |
34 |
|
154,167,169 |
546,963 |
– |
– |
– |
154,714,132 |
| Government securities |
|
|
154,167,169 |
|
– |
– |
– |
154,167,169 |
| Quoted shares |
|
|
|
500,278 |
– |
– |
– |
500,278 |
| Unquoted shares |
|
|
|
46,685 |
– |
– |
– |
46,685 |
| Investment in unit trust |
|
|
|
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Financial investments –
Held to maturity |
35 |
|
63,562,752 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
63,562,752 |
| Government securities |
|
|
63,562,752 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
63,562,752 |
| Other investments |
|
|
|
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Financial investments –
Loans and receivables |
36 |
|
40,566,702 |
8,145,775 |
– |
– |
– |
48,712,477 |
| Government securities |
|
|
40,566,702 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
40,566,702 |
| Other investments |
|
|
|
8,145,775 |
– |
– |
– |
8,145,775 |
| Total |
|
|
305,455,945 |
531,869,363 |
245,165,520 |
9,800,801 |
15,189,594 |
1,107,481,223 |
Definition of “Past Due” – The Bank considers that any amounts uncollected one day or more beyond their contractual due date.
| As at December 31, 2016 |
|
|
Neither past due nor individually impaired |
|
|
|
Note |
|
Government
guarantee |
Investment
grade |
Moderate risk |
Past due but not
individually
impaired |
Individually
impaired |
Total |
|
|
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Cash and cash equivalents |
27 |
|
– |
30,193,589 |
– |
– |
– |
30,193,589 |
| Balances with central banks |
28 |
|
43,873,205 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
43,873,205 |
| Placements with banks |
29 |
|
– |
11,718,499 |
– |
– |
– |
11,718,499 |
Securities purchased under
resale agreements |
|
|
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Derivative financial assets |
30 |
|
– |
1,052,829 |
– |
– |
– |
1,052,829 |
Other financial instruments –
Held for trading |
31 |
|
3,505,335 |
293,809 |
1,188,654 |
– |
– |
4,987,798 |
Loans and receivables
to banks |
32 |
|
|
– |
624,458 |
|
|
624,458 |
Loans and receivables to
other customers |
33 |
|
– |
375,317,855 |
216,881,465 |
10,170,288 |
13,648,620 |
616,018,228 |
| Corporate banking |
|
|
– |
194,301,767 |
69,668,628 |
6,354,171 |
4,144,273 |
274,468,839 |
| Amortised cost |
|
|
– |
195,783,488 |
70,296,607 |
6,850,195 |
7,095,590 |
280,025,880 |
Less – Provision for
impairment |
|
|
– |
1,481,721 |
627,979 |
496,024 |
2,951,317 |
5,557,041 |
| Personal banking |
|
|
– |
181,016,088 |
147,212,837 |
3,816,117 |
9,504,347 |
341,549,389 |
| Amortised cost |
|
|
– |
181,729,813 |
148,095,904 |
8,532,823 |
15,006,487 |
353,365,027 |
Less – Provision for
impairment |
|
|
– |
713,725 |
883,067 |
4,716,706 |
5,502,140 |
11,815,638 |
Financial investments –
Available for sale |
34 |
|
159,573,316 |
450,155 |
– |
– |
– |
160,023,471 |
| Government securities |
|
|
159,573,316 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
159,573,316 |
| Quoted shares |
|
|
– |
246,548 |
– |
– |
– |
246,548 |
| Unquoted shares |
|
|
– |
47,147 |
– |
– |
– |
47,147 |
| Investment in unit trust |
|
|
– |
156,460 |
– |
– |
– |
156,460 |
Financial investments –
Held to maturity |
35 |
|
60,981,298 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
60,981,298 |
| Government securities |
|
|
60,981,298 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
60,981,298 |
| Other investments |
|
|
|
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Financial investments –
Loans and receivables |
36 |
|
40,076,392 |
11,747,634 |
– |
– |
– |
51,824,026 |
| Government securities |
|
|
40,076,392 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
40,076,392 |
| Other investments |
|
|
|
11,747,634 |
– |
– |
– |
11,747,634 |
| Total |
|
|
308,009,546 |
430,774,370 |
218,694,577 |
10,170,288 |
13,648,620 |
981,297,401 |
Definition of “Past Due” – The Bank considers that any amount uncollected one day or more beyond their contractual due date.
69.1.1 (e) Trading assets
Held-for-trading investments in debt and equity securities
The table below sets out the credit quality of debt and equity securities classified as held for trading securities which include investments made by the Bank in Government Securities of Sri Lanka and Bangladesh. The analysis of equity securities is based on Fitch Ratings Nomenclature or Equivalent Ratings, where applicable.
| As at December 31, |
|
|
2017 |
2016 |
|
Note |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Government securities |
|
|
|
|
| Government securities – Sri Lanka |
|
|
|
|
| Treasury bills |
|
|
654,438 |
1,761,970 |
| Treasury bonds |
|
|
1,703,438 |
1,743,365 |
| Government securities – Bangladesh |
|
|
|
|
| Treasury bills |
|
|
278,618 |
705,251 |
| Treasury bonds |
|
|
1,459,674 |
483,403 |
| Total – Government securities |
|
|
4,096,168 |
4,693,989 |
| Equity securities |
|
|
|
|
| Rated AAA |
|
|
12,341 |
9,966 |
| Rated AA+ to AA- |
|
|
16,492 |
19 |
| Rated A+ to A |
|
|
60,879 |
86,970 |
| Rated BBB+ |
|
|
5,710 |
– |
| Unrated |
|
|
219,323 |
196,854 |
| Total – Equity securities |
|
|
314,745 |
293,809 |
| Total |
31 |
|
4,410,913 |
4,987,798 |
Credit exposure arising from derivative transactions
Credit risk arising from derivative financial instruments at any time is limited to those with positive fair values, as reported in the Statement of Financial Position. With gross settled derivatives, the Bank is also exposed to a settlement risk, being the risk that the counterparty failing to deliver the counter value.
The tables below show analysis of credit exposures arising from derivative financial assets and liabilities.
| As at December 31,2017 |
Derivative Type |
|
|
Forward |
SWAPS |
Spot |
Total |
|
Notional
amount |
Fair
value |
Notional
amount |
Fair
value |
Notional
amount |
Fair
value |
Notional
amount |
Fair
value |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Derivative financial assets (Note 1) |
35,831,935 |
1,264,900 |
80,896,084 |
1,067,259 |
4,432,721 |
2,377 |
121,160,740 |
2,334,536 |
| Derivative financial liabilities (Note 2) |
26,602,410 |
(1,015,648) |
83,904,746 |
(2,660,838) |
1,569,843 |
(2,008) |
112,076,999 |
(3,678,494) |
| Note 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Derivative financial assets by counterparty type |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| With banks |
10,081,268 |
170,229 |
78,629,102 |
972,827 |
3,617,099 |
2,375 |
92,327,469 |
1,145,431 |
| Other customers |
25,750,667 |
1,094,671 |
2,266,982 |
94,432 |
815,622 |
2 |
28,833,271 |
1,189,105 |
|
35,831,935 |
1,264,900 |
80,896,084 |
1,067,259 |
4,432,721 |
2,377 |
121,160,740 |
2,334,536 |
| Note 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Derivative financial liabilities by counterparty type |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| With banks |
3,146,244 |
(61,900) |
83,904,746 |
(2,660,838) |
1,569,843 |
(2,008) |
88,620,833 |
(2,724,746) |
| Other customers |
23,456,166 |
(953,748) |
– |
– |
– |
– |
23,456,166 |
(953,748) |
|
26,602,410 |
(1,015,648) |
83,904,746 |
(2,660,838) |
1,569,843 |
(2,008) |
112,076,999 |
(3,678,494) |
| As at December 31,2016 |
Derivative type |
|
|
Forward |
SWAPS |
Spot |
Total |
|
Notional
amount |
Fair
value |
Notional
amount |
Fair
value |
Notional
amount |
Fair
value |
Notional
amount |
Fair
value |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Derivative financial assets (Note 1) |
45,610,942 |
788,808 |
61,841,987 |
261,664 |
2,713,810 |
2,357 |
110,166,739 |
1,052,829 |
| Derivative financial liabilities (Note 2) |
20,808,137 |
(849,010) |
96,170,047 |
(663,714) |
1,513,965 |
(2,311) |
118,492,149 |
(1,515,035) |
| Note 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Derivative financial assets by counterparty type |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| With banks |
12,618,500 |
98,281 |
56,881,672 |
247,217 |
2,352,621 |
2,258 |
71,852,793 |
347,756 |
| Other customers |
32,992,442 |
690,527 |
4,960,315 |
14,447 |
361,189 |
99 |
38,313,946 |
705,073 |
|
45,610,942 |
788,808 |
61,841,987 |
261,664 |
2,713,810 |
2,357 |
110,166,739 |
1,052,829 |
| Note 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Derivative financial liabilities by counterparty type |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| With banks |
8,910,120 |
(38,476) |
93,952,339 |
(654,910) |
1,513,965 |
(2,311) |
104,376,424 |
(695,697) |
| Other customers |
11,898,017 |
(810,534) |
2,217,708 |
(8,804) |
– |
– |
14,115,725 |
(819,338) |
|
20,808,137 |
(849,010) |
96,170,047 |
(663,714) |
1,513,965 |
(2,311) |
118,492,149 |
(1,515,035) |
69.1.2 Impaired loans and receivables and investment in debt securities
Reconciliation of changes in the carrying amount of individually impaired loans and receivables as detailed below:
| As at December 31, |
2017 |
2016 |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Impaired loans and receivables to other customers as at January 1, |
13,648,620 |
6,376,669 |
| Newly classified as impaired loans and receivables during the year |
8,177,859 |
9,802,478 |
| Net change in already impaired loans and receivables during the year |
361,095 |
(281,599) |
| Net payment, write-off and recoveries and other movements during the year |
(6,997,980) |
(2,248,928) |
| Impaired loans and receivables to customers as at December 31, |
15,189,594 |
13,648,620 |
No impairment provision has been made for investment in debt securities as at December 31, 2017 (2016 – Nil).
Refer Note 18 for methodology of impairment assessment, on “Impairment of Financial Assets” which are carried at amortised cost.
Details of provision for impairment for loans and receivables to banks and for loans and receivable to other customers, are detailed in
Notes 32 and 33.
Set out below is an analysis of the gross and net carrying amounts of individually impaired loans and receivables by risk rating.
| As at December 31, |
2017 |
2016 |
|
Loans and receivable to customers |
Loans and receivable to customers |
|
Gross |
Net |
Gross |
Net |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Rating 0-4: Investment grade |
4,613,603 |
4,470,693 |
4,766,976 |
4,607,959 |
| Rating 5-6: Moderate risk |
4,713,404 |
4,600,908 |
4,046,553 |
3,912,239 |
| Rating S: High risk |
763,567 |
642,017 |
615,456 |
402,464 |
| Rating 7-9: Extreme risk |
12,952,674 |
5,475,976 |
12,673,092 |
4,725,958 |
| Total |
23,043,248 |
15,189,594 |
22,102,077 |
13,648,620 |
69.1.3 Collaterals held
Loan to value ratio of residential mortgage lending
The table below stratifies mortgaged credit exposures to retail customers by ranges of loan-to-value (LTV) ratio. LTV is calculated as the ratio of the gross amount of the loan to the value of the collateral, which is used for the computation of Capital Adequacy Ratios. The value of the collateral for residential mortgage loans is based on the forced sale value determined by professional valuers.
| As at December 31, |
2017 |
2016 |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Composition (%) |
Rs. ’000 |
Composition (%) |
| LTV ratio |
|
|
|
|
| Less than 50% |
11,804,905 |
29.83 |
8,406,374 |
26.14 |
| 51 - 70% |
8,952,662 |
22.62 |
7,027,873 |
21.86 |
| 71 - 90% |
10,466,905 |
26.45 |
8,262,704 |
25.70 |
| 91 - 100% |
1,600,415 |
4.05 |
1,352,172 |
4.20 |
| More than 100%* |
6,745,986 |
17.05 |
7,105,439 |
22.10 |
|
39,570,873 |
100.00 |
32,154,562 |
100.00 |
* LTV ratio more than 100% has arisen due to subsequent disbursements made to the borrower after the initial valuation of the property (the denominator).
Assets obtained by taking the possession of collaterals
Repossession of collaterals is resorted to extreme situations where action is necessitated to recover the dues. The repossessed assets are disposed, in an orderly and transparent manner and the proceeds are used to reduce or recover the outstanding claims and the amount recovered in excess of the dues is refunded to the customer.
69.1.4 Concentration of credit risk
By setting various concentration limits under different criteria within the established risk appetite framework (i.e., single borrower/group,
industry sectors, product, counterparty and country etc.), the Bank ensures that an acceptable level of risk diversification is maintained
on an ongoing basis. These limits are continuously monitored and periodically reviewed by the Credit Policy Committee, the Executive
Integrated Risk Management Committee and the Board Integrated Risk Management Committee to capture the developments in the
market, political and economic environment both locally and globally to strengthen the dynamic portfolio management practices and
to provide an early warning on possible credit concentrations.
The maximum exposure to credit risk in respect of each item of financial assets in the Statement of Financial Position as at December 31,
as per industry sector and by geographical region of financial assets is given below:
69.1.4 (a) Industry-wise distribution
As at
December 31,
2017 |
Agriculture
and
fishing |
Manu-
facturing |
Tourism |
Transport |
Construction |
Traders |
New
economy |
Financial
and
business
services |
Government |
Infrastructure |
Other
services |
Other
customers |
Total |
| Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Financial assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash
equivalents |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
33,224,619 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
33,224,619 |
Balances with
central banks |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
|
44,801,446 |
– |
– |
– |
44,801,446 |
Placements
with banks |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
17,633,269 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
17,633,269 |
Securities
purchased under
resale agreements |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Derivative
financial assets |
– |
2,261 |
– |
– |
– |
586,294 |
– |
1,745,507 |
– |
– |
474 |
– |
2,334,536 |
Other financial
instruments –
Held for trading |
– |
107,107 |
5,732 |
– |
27,781 |
26,674 |
48,207 |
78,102 |
4,096,168 |
21,142 |
– |
– |
4,410,913 |
Government
Securities |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
4,096,168 |
– |
– |
– |
4,096,168 |
Quoted equity
securities |
– |
107,107 |
5,732 |
– |
27,781 |
26,674 |
48,207 |
78,102 |
– |
21,142 |
– |
– |
314,745 |
Loans and
receivables to
banks |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
640,512 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
640,512 |
Loans and
receivables to
other customers* |
68,713,903 |
112,807,745 |
44,937,470 |
16,820,822 |
104,314,394 |
110,304,070 |
17,031,993 |
47,045,113 |
– |
20,086,388 |
62,567,873 |
132,816,796 |
737,446,567 |
Financial
investments –
Available for sale |
– |
13,213 |
– |
– |
141,093 |
– |
– |
392,657 |
154,167,169 |
– |
– |
– |
154,714,132 |
Government
securities |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
154,167,169 |
– |
– |
– |
154,167,169 |
Equity securities –
Quoted shares |
– |
13,213 |
– |
– |
141,093 |
– |
– |
345,972 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
500,278 |
Equity securities –
Unquoted shares |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
46,685 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
46,685 |
Investment in
unit trusts |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Financial
investments –
Held to maturity |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
63,562,752 |
– |
– |
– |
63,562,752 |
Government
securities |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
63,562,752 |
– |
– |
– |
63,562,752 |
Financial
investments –
Loans and
receivables |
– |
2,233,016 |
– |
– |
– |
997,423 |
– |
4,678,169 |
40,566,702 |
– |
237,167 |
– |
48,712,477 |
Government
securities |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
40,566,702 |
– |
– |
– |
40,566,702 |
| Other investments |
– |
2,233,016 |
– |
– |
– |
997,423 |
– |
4,678,169 |
– |
– |
237,167 |
– |
8,145,775 |
| Total |
68,713,903 |
115,163,342 |
44,943,202 |
16,820,822 |
104,483,268 |
111,914,461 |
17,080,200 |
105,437,948 |
307,194,237 |
20,107,530 |
62,805,514 |
132,816,796 |
1,107,481,223 |
(*) Loans and advances referred to above do not agree with the Note 33.1 (c) due to impairment provisions.
As at
December 31,
2016 |
Agriculture
and
fishing |
Manufacturing |
Tourism |
Transport |
Construction |
Traders |
New
economy |
Financial
and
business
services |
Government |
Infrastructure |
Other
services |
Other
customers |
Total |
| Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Financial assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash
equivalents |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
30,193,589 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
30,193,589 |
Balances with
central banks |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
|
43,873,205 |
– |
– |
– |
43,873,205 |
Placements
with banks |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
11,718,499 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
11,718,499 |
Securities
purchased under
resale agreements |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Derivative
financial assets |
– |
86,050 |
– |
– |
– |
180,305 |
– |
757,311 |
– |
– |
29,163 |
– |
1,052,829 |
Other financial
instruments –
Held for trading |
– |
115,386 |
8,269 |
– |
8,487 |
30,707 |
28,912 |
77,933 |
4,693,989 |
24,115 |
– |
– |
4,987,798 |
Government
securities |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
4,693,989 |
– |
– |
– |
4,693,989 |
Quoted securities –
Quoted shares |
– |
115,386 |
8,269 |
– |
8,487 |
30,707 |
28,912 |
77,933 |
– |
24,115 |
– |
– |
293,809 |
Loans and
receivables to
banks |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
624,458 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
624,458 |
Loans and
receivables to
other customers* |
61,601,062 |
89,467,955 |
43,784,446 |
14,493,562 |
78,831,928 |
90,502,006 |
14,664,164 |
49,133,741 |
– |
17,805,741 |
56,263,732 |
99,469,891 |
616,018,228 |
Financial
investments –
Available for sale |
– |
14,427 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
435,728 |
159,573,316 |
– |
– |
– |
160,023,471 |
Government
securities |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
159,573,316 |
– |
– |
– |
159,573,316 |
Equity securities –
Quoted shares |
– |
14,427 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
232,121 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
246,548 |
Equity securities –
Unquoted shares |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
47,147 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
47,147 |
Investment in
unit trust |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
156,460 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
156,460 |
Financial
investments –
Held to maturity |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
60,981,298 |
– |
– |
– |
60,981,298 |
Government
securities |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
60,981,298 |
– |
– |
– |
60,981,298 |
Financial
investments –
Loans and
receivables |
– |
2,584,717 |
– |
– |
– |
998,155 |
– |
7,927,595 |
40,076,392 |
– |
237,167 |
– |
51,824,026 |
Government
securities |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
40,076,392 |
– |
– |
– |
40,076,392 |
| Other investments |
– |
2,584,717 |
– |
– |
– |
998,155 |
– |
7,927,595 |
– |
– |
237,167 |
– |
11,747,634 |
| Total |
61,601,062 |
92,268,535 |
43,792,715 |
14,493,562 |
78,840,415 |
91,711,173 |
14,693,076 |
100,868,854 |
309,198,200 |
17,829,856 |
56,530,062 |
99,469,891 |
981,297,401 |
(*) Loans and advances referred to above do not agree with the Note 33.1 (c) due to impairment provisions.
69.1.4 (b) Geographical distribution of loans and receivable portfolio
The Western Province has recorded a higher percentage of lending based on geographical distribution of the Bank’s lending portfolio. It has accounted for 77% (approximately) of total advances portfolio of the Bank (excluding Bangladesh operations) as at December 31, 2017. Although, Western Province is attracted with highest credit concentration, we believe that a sizable portion of these lending has been utilised to facilitate industries scattered around the country. For example, most of the large corporates which have island-wide operations are being accommodated by the Branches and Corporate Banking Division situated in the Western Province and thereby reflecting a fairly diversified geographical concentration contrary to the figures given below:
As at December 31, 2017
| Country/province |
Loans and Receivables by Product |
|
Overdrafts
Rs. ’000 |
Trade
finance
Rs. ’000 |
Lease
receivables
Rs. ’000 |
Credit
cards
Rs. ’000 |
Pawning
Rs. ’000 |
Staff
loans
Rs. ’000 |
Housing
loans
Rs. ’000 |
Personal
loans
Rs. ’000 |
Long-Term
loans
Rs. ’000 |
Short-Term
loans
Rs. ’000 |
Bills of
exchange
Rs. ’000 |
Total
Rs. ’000 |
| Sri Lanka |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Central |
9,105,845 |
234,423 |
1,916,498 |
411,761 |
45,545 |
– |
3,068,331 |
1,477,341 |
18,850,775 |
1,475,025 |
10,947 |
36,596,491 |
| Eastern |
1,117,710 |
30,735 |
627,422 |
96,299 |
24,244 |
– |
359,754 |
530,338 |
2,204,475 |
138,066 |
– |
5,129,043 |
| North Central |
1,106,922 |
87,888 |
1,502,978 |
105,245 |
9,554 |
– |
563,567 |
424,136 |
5,643,030 |
369,027 |
– |
9,812,347 |
| Northern |
2,526,778 |
95,605 |
1,216,214 |
117,523 |
430,787 |
– |
737,940 |
777,142 |
3,536,515 |
434,081 |
– |
9,872,585 |
| North Western |
6,748,789 |
948,591 |
2,956,376 |
356,880 |
117,380 |
– |
3,301,358 |
1,833,343 |
12,636,399 |
1,737,537 |
8,657 |
30,645,310 |
| Sabaragamuwa |
5,023,234 |
544,685 |
2,638,106 |
213,385 |
46,153 |
– |
2,863,952 |
950,615 |
8,441,449 |
805,885 |
137,733 |
21,665,197 |
| Southern |
6,014,775 |
1,464,661 |
3,603,623 |
388,474 |
89,707 |
– |
4,908,557 |
1,948,311 |
13,632,876 |
968,028 |
10,519 |
33,029,531 |
| Uva |
1,516,886 |
25,906 |
1,006,287 |
121,106 |
16,417 |
– |
1,832,132 |
629,553 |
4,376,394 |
425,507 |
- |
9,950,188 |
| Western |
76,142,919 |
50,154,096 |
21,747,218 |
6,956,843 |
555,710 |
7,831,111 |
34,700,747 |
18,696,937 |
225,372,988 |
75,412,905 |
3,941,857 |
521,513,331 |
| Bangladesh |
5,193,417 |
3,925,396 |
258,288 |
58,047 |
– |
117,336 |
476,542 |
385,564 |
10,368,545 |
25,758,410 |
12,690,999 |
59,232,544 |
| Total |
114,497,275 |
57,511,986 |
37,473,010 |
8,825,563 |
1,335,497 |
7,948,447 |
52,812,880 |
27,653,280 |
305,063,446 |
107,524,471 |
16,800,712 |
737,446,567 |
As at December 31, 2016
| Country/province |
Loans and Receivables by Product |
|
Overdrafts
Rs. ’000 |
Trade
finance
Rs. ’000 |
Lease
receivables
Rs. ’000 |
Credit
cards
Rs. ’000 |
Pawning
Rs. ’000 |
Staff
loans
Rs. ’000 |
Housing
loans
Rs. ’000 |
Personal
loans
Rs. ’000 |
Long-Term
loans
Rs. ’000 |
Short-Term
loans
Rs. ’000 |
Bills of
exchange
Rs. ’000 |
Total
Rs. ’000 |
| Sri Lanka |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Central |
10,661,557 |
178,668 |
1,942,902 |
323,715 |
52,966 |
– |
2,787,403 |
1,374,071 |
16,327,523 |
953,154 |
30,441 |
34,632,400 |
| Eastern |
832,420 |
91,427 |
428,517 |
69,867 |
13,091 |
– |
286,271 |
407,103 |
1,933,866 |
34,492 |
– |
4,097,054 |
| North Central |
946,600 |
104,482 |
1,534,704 |
79,938 |
7,219 |
– |
423,027 |
293,058 |
4,584,201 |
201,547 |
4,433 |
8,179,209 |
| Northern |
2,004,596 |
148 |
792,854 |
90,711 |
352,881 |
– |
619,791 |
614,333 |
3,070,477 |
40,954 |
– |
7,586,745 |
| North Western |
4,761,332 |
522,114 |
2,633,365 |
270,788 |
121,944 |
– |
2,982,527 |
1,483,099 |
11,563,070 |
714,417 |
13,287 |
25,065,943 |
| Sabaragamuwa |
4,571,645 |
289,939 |
2,334,374 |
165,686 |
53,744 |
– |
2,430,909 |
865,355 |
7,917,406 |
427,456 |
3,025 |
19,059,539 |
| Southern |
5,137,398 |
1,380,610 |
3,022,169 |
329,615 |
83,428 |
– |
4,472,432 |
1,803,027 |
12,331,936 |
327,570 |
976 |
28,889,161 |
| Uva |
1,226,155 |
31,070 |
963,565 |
92,241 |
17,990 |
– |
1,600,487 |
551,923 |
3,505,996 |
220,512 |
1,248 |
8,211,187 |
| Western |
64,168,727 |
38,940,278 |
21,660,085 |
4,646,051 |
532,526 |
7,144,946 |
30,661,911 |
17,701,287 |
201,515,731 |
43,616,020 |
3,571,804 |
434,159,366 |
| Bangladesh |
3,793,007 |
704,416 |
177,863 |
68,234 |
– |
106,066 |
221,024 |
276,508 |
8,720,126 |
23,435,538 |
8,634,842 |
46,137,624 |
| Total |
98,103,437 |
42,243,152 |
35,490,398 |
6,136,846 |
1,235,789 |
7,251,012 |
46,485,782 |
25,369,764 |
271,470,332 |
69,971,660 |
12,260,056 |
616,018,228 |
Please refer Note 33 for the gross carrying amount of the loans and advances.
69.1.5 Exposures to unrated countries
This note summarises the Bank’s on-balance sheet and off-balance sheet exposure to countries which are not rated by
an established rating company.
| As at December 31, |
2017 |
2016 |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| On-balance sheet exposures |
|
|
| Loans and receivables to customers |
|
|
| At net carrying amount |
294,567 |
253,978 |
| Gross carrying value |
296,249 |
254,534 |
| Less – Provision for impairment |
1,682 |
556 |
| At fair value net of provision for impairment (*) |
294,567 |
253,978 |
| Fair value before impairment |
296,249 |
254,534 |
| Less – Provision for impairment |
1,682 |
556 |
| Off-balance sheet exposures |
|
|
| Loan commitments and contingencies |
– |
– |
| Contingencies |
– |
– |
| Loan commitments |
– |
– |
| Total on-balance sheet and off-balance sheet exposure |
294,567 |
253,978 |
(*) There is no difference between the net carrying amount and the fair value, as all facilities have been granted under floating interest rates.
69.2 Liquidity risk
Liquidity risk is the Bank’s inability to meet On or Off-Balance Sheet contractual and contingent financial obligations, as they fall due without incurring unacceptable losses. The principal objective in liquidity risk management is to assess the need for funds to meet such obligations and to ensure the availability of adequate funding to fulfil those needs at the appropriate time, under both normal and stressed conditions.
Therefore, the Bank continuously analyses and monitors its liquidity profile, maintains adequate levels of high quality liquid assets, ensures access to diverse funding sources and has contingency funding agreements with peer banks to meet any unforeseen liquidity requirements. Exposures and ratios against tolerance limits as well as stressed scenarios are regularly monitored in order to identify the Bank’s liquidity position and potential funding requirements.
Assets and Liability Management Committee (ALCO)
ALCO chaired by the Managing Director, has representatives from Treasury, Corporate Banking, Personal Banking, Risk and Finance Departments. The Committee meets fortnightly or more frequently to monitor and manage the assets and liabilities of the Bank and also the overall liquidity position to keep the Bank’s liquidity at healthy levels, whilst satisfying the regulatory requirements.
69.2.1 Exposure to liquidity risk
The key measure used by the Bank for managing liquidity risk is the ratio of liquid assets to total liabilities excluding shareholders’ funds.
For this purpose, “liquid assets” mainly comprise cash and cash equivalents, placements with banks and Government Securities (net). Details of the reported ratio of liquid assets to external liabilities of the Domestic Banking Unit (DBU) and the Off-shore Banking Centre (OBC) as at the reporting dates are as follows:
|
DBU |
OBC |
|
2017
% |
2016
% |
2017
% |
2016
% |
| As at December 31, |
27.28 |
27.19 |
30.95 |
30.19 |
| Average for the period |
26.66 |
25.63 |
31.72 |
35.78 |
| Maximum for the period |
27.98 |
27.19 |
37.00 |
47.13 |
| Minimum for the period |
25.75 |
23.88 |
27.80 |
28.84 |
| Statutory minimum requirement |
20.00 |
20.00 |
20.00 |
20.00 |
The graph below depicts the trends in liquidity ratios of the Bank calculated on a quarterly basis during the period from December 2015 to December 2017:
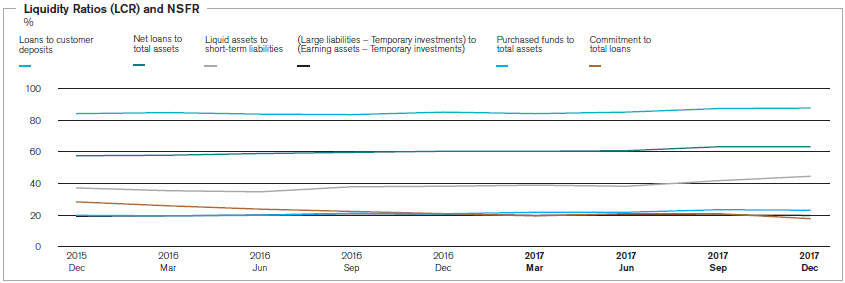
69.2.2 Maturity analysis of financial assets and financial liabilities
69.2.2 (a) Remaining contractual period to maturity – Bank
(i) Remaining contractual period to maturity of the assets employed by the Bank as at December 31, is detailed below:
| As at December 31, |
Up to 3
months |
3 to 12
months |
1 to 3
years |
3 to 5
years |
More than
5 years |
Total as at
31.12.2017 |
Total as at
31.12.2016 |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Interest earning assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Financial assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Cash and cash equivalents |
3,457,539 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
3,457,539 |
7,930,050 |
| Balances with central banks |
887,551 |
263,830 |
– |
4,607 |
– |
1,155,988 |
498,616 |
| Placements with banks |
17,633,269 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
17,633,269 |
11,718,499 |
Securities purchased under
resale agreements |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Derivative financial assets |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Other financial instruments –
Held-for-trading |
4,096,168 |
|
|
|
|
4,096,168 |
4,693,989 |
| Loans and receivables to banks |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Loans and receivables to
other customers |
231,342,860 |
198,426,781 |
169,978,799 |
93,774,191 |
43,923,936 |
737,446,567 |
616,018,228 |
Financial investments –
Available-for-sale |
13,025,195 |
67,787,547 |
59,124,910 |
14,229,518 |
– |
154,167,170 |
159,573,316 |
Financial investments –
Held-to-maturity |
4,077,407 |
9,871,844 |
12,885,249 |
29,661,652 |
7,066,600 |
63,562,752 |
60,981,298 |
Financial investments –
Loans and receivables |
2,521,780 |
5,188,975 |
16,430,329 |
24,571,393 |
– |
48,712,477 |
51,824,026 |
Total interest earning assets
as at December 31, 2017 |
277,041,769 |
281,538,977 |
258,419,287 |
162,241,361 |
50,990,536 |
1,030,231,930 |
|
Total interest earning assets
as at December 31, 2016 |
276,268,527 |
174,556,015 |
269,347,751 |
113,511,379 |
79,554,350 |
|
913,238,022 |
| Non-interest earning assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Financial assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Cash and cash equivalents |
29,767,080 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
29,767,080 |
22,263,539 |
| Balances with central banks |
26,999,348 |
14,321,349 |
783,669 |
730,063 |
811,029 |
43,645,458 |
43,374,589 |
| Placements with banks |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Securities purchased under
resale agreements |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Derivative financial assets |
959,937 |
1,374,599 |
– |
– |
– |
2,334,536 |
1,052,829 |
Other financial instruments –
Held for trading |
314,745 |
|
|
|
|
314,745 |
293,809 |
| Loans and receivables to banks |
– |
– |
640,512 |
– |
– |
640,512 |
624,458 |
Loans and receivables to other
customers |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Financial investments –
Available for sale |
– |
– |
– |
17,491 |
529,471 |
546,962 |
450,155 |
Financial investments –
Held to maturity |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Financial investments –
Loans and receivables |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Non-financial assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Investments in subsidiaries |
– |
– |
– |
– |
3,065,935 |
3,065,935 |
2,435,392 |
| Investments in associates |
– |
– |
– |
– |
44,331 |
44,331 |
44,331 |
| Property, plant and equipment |
– |
– |
– |
– |
14,634,710 |
14,634,710 |
10,307,825 |
| Intangible assets |
– |
– |
– |
– |
776,810 |
776,810 |
640,645 |
| Leasehold property |
– |
– |
– |
– |
72,594 |
72,594 |
73,536 |
| Deferred tax assets |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
963,935 |
| Other assets |
12,270,707 |
257,173 |
1,245,002 |
506,177 |
3,019,103 |
17,298,162 |
16,438,166 |
| Total non-interest earning assets as at December 31, 2017 |
70,311,817 |
15,953,121 |
2,669,183 |
1,253,731 |
22,953,983 |
113,141,835 |
|
| Total non-interest earning assets as at December 31, 2016 |
62,243,958 |
14,616,440 |
3,826,664 |
991,974 |
17,284,173 |
|
98,963,209 |
| Total assets – as at December 31, 2017 |
347,353,586 |
297,492,098 |
261,088,470 |
163,495,092 |
73,944,519 |
1,143,373,765 |
|
| Total assets – as at December 31, 2016 |
338,512,485 |
189,172,455 |
273,174,415 |
114,503,353 |
96,838,523 |
|
1,012,201,231 |
| Percentage – as at December 31, 2017 (*) |
30.38 |
26.02 |
22.83 |
14.30 |
6.47 |
100.00 |
|
| Percentage – as at December 31, 2016 (*) |
33.44 |
18.69 |
26.99 |
11.31 |
9.57 |
|
100.00 |
(*) Total assets of each maturity bucket as a percentage of total assets employed by the Bank.
(ii) Remaining contractual period to maturity of the liabilities and shareholders’ funds employed by the Bank as at the date of Statement of Financial Position is detailed below:
| As at December 31, |
Up to 3
months |
3 to 12
months |
1 to 3
years |
3 to 5
years |
More than
5 years |
Total as at
31.12.2017 |
Total as at
31.12.2016 |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Interest-bearing liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Financial liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Due to banks |
32,840,250 |
3,840,696 |
12,232,304 |
– |
41,224 |
48,954,474 |
63,523,388 |
| Derivative financial liabilities |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Securities sold under
repurchase agreements |
35,951,132 |
10,978,972 |
2,746,663 |
– |
– |
49,676,767 |
69,867,469 |
| Other financial liabilities – Held-for-trading |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Due to other customers/
deposits from customers |
455,218,755 |
288,988,744 |
18,492,159 |
13,050,348 |
13,783,280 |
789,533,286 |
683,569,052 |
| Other borrowings |
657,813 |
2,091,720 |
5,021,093 |
7,503,789 |
8,511,679 |
23,786,094 |
9,270,154 |
| Subordinated liabilities |
203,326 |
314,552 |
– |
9,477,720 |
15,170,326 |
25,165,924 |
24,849,539 |
Total interest-bearing liabilities
as at December 31, 2017 |
524,871,276 |
306,214,684 |
38,492,219 |
30,031,857 |
37,506,509 |
937,116,545 |
|
Total interest-bearing liabilities
as at December 31, 2016 |
504,725,495 |
263,099,940 |
31,662,332 |
21,783,917 |
29,807,918 |
|
851,079,602 |
| Non-interest bearing liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Financial liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Due to banks |
8,166,517 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
8,166,517 |
4,085,423 |
| Derivative financial liabilities |
2,488,462 |
1,185,570 |
– |
– |
4,462 |
3,678,494 |
1,515,035 |
Securities sold under
repurchase agreements |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Other financial liabilities –
Held-for-trading |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Due to other customers/deposits
from customers |
60,594,225 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
60,594,225 |
55,994,442 |
| Other borrowings |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Subordinated liabilities |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Non-financial liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Current tax liabilities |
798,084 |
3,345,827 |
– |
– |
– |
4,143,911 |
3,440,736 |
| Deferred tax |
182,545 |
153,861 |
588,908 |
261,930 |
2,087,582 |
3,274,826 |
– |
| Other provisions |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
1,874 |
| Other liabilities |
3,071,733 |
9,738,767 |
2,943,111 |
1,374,896 |
2,096,857 |
19,225,364 |
17,710,394 |
| Due to subsidiaries |
74,523 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
74,523 |
20,061 |
| Equity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Stated capital |
– |
– |
– |
– |
37,143,541 |
37,143,541 |
24,978,003 |
| Statutory reserves |
– |
– |
– |
– |
6,476,952 |
6,476,952 |
5,647,890 |
| Retained earnings |
– |
– |
– |
– |
4,987,446 |
4,987,446 |
4,464,077 |
| Other reserves |
– |
– |
– |
– |
58,491,421 |
58,491,421 |
43,263,694 |
| Total non-interest bearing liabilities as at December 31, 2017 |
75,376,089 |
14,424,025 |
3,532,019 |
1,636,826 |
111,288,261 |
206,257,220 |
|
Total non-interest bearing liabilities
as at December 31, 2016 |
76,696,128 |
3,058,595 |
1,529,112 |
309,278 |
79,528,516 |
|
161,121,629 |
| Total liabilities and equity – as at December 31, 2017 |
600,247,365 |
320,638,709 |
42,024,238 |
31,668,683 |
148,794,770 |
1,143,373,765 |
|
| Total liabilities and equity – as at December 31, 2016 |
581,421,623 |
266,158,535 |
33,191,444 |
22,093,195 |
109,336,434 |
|
1,012,201,231 |
| Percentage – as at December 31, 2017 (*) |
52.50 |
28.04 |
3.68 |
2.77 |
13.01 |
100.00 |
|
| Percentage – as at December 31, 2016 (*) |
57.44 |
26.30 |
3.28 |
2.18 |
10.80 |
|
100.00 |
(*) Total liabilities and shareholders’ funds of each maturity bucket as a percentage of total liabilities and shareholders’ funds employed by the Bank.
69.2.2 (b) Non-derivative financial assets and financial liabilities expected to be recovered or settled after 12 months from the reporting date
The table below sets out the carrying amounts of non-derivative financial assets and financial liabilities expected to be recovered or settled after 12 months from the Reporting date:
| As at December 31, |
2017 |
2016 |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Financial assets |
|
|
| Non-derivative financial assets |
|
|
| Balances with central banks |
2,329,368 |
2,459,890 |
| Loans and receivables to banks |
640,512 |
624,458 |
| Loans and receivables to other customers |
307,676,926 |
272,097,889 |
| Financial investments – Available for sale |
73,901,390 |
114,074,408 |
| Financial investments – Held to maturity |
49,613,501 |
56,725,526 |
| Total |
434,161,697 |
445,982,171 |
| Financial liabilities |
|
|
| Non-derivative financial liabilities |
|
|
| Securities sold under repurchase agreements |
2,746,663 |
11,019 |
| Due to other customers/deposits from customers |
45,325,787 |
40,211,606 |
| Other borrowings |
21,036,561 |
6,721,530 |
| Subordinated liabilities |
24,630,973 |
24,330,012 |
| Total |
93,739,984 |
71,274,167 |
69.2.3 Liquidity reserves
The table below sets out the components of the Bank’s liquidity reserves:
| As at December 31, |
2017 |
2016 |
|
Carrying amount
Rs. ’000 |
Fair value
Rs. ’000 |
Carrying amount
Rs. ’000 |
Fair value
Rs. ’000 |
| Balances with central banks |
44,801,446 |
44,801,446 |
43,873,205 |
43,873,205 |
| Cash and balances with other banks |
9,944,020 |
9,944,020 |
12,786,813 |
12,786,813 |
| Coins and notes held |
23,280,599 |
23,280,599 |
17,406,776 |
17,406,776 |
| Unencumbered debt securities issued by sovereigns |
172,149,322 |
171,675,912 |
155,381,134 |
151,455,447 |
| Total |
250,175,387 |
249,701,977 |
229,447,928 |
225,522,241 |
69.2.4 Financial assets available to support future funding
The table below sets out the availability of the Bank’s financial assets to support future funding:
| As at December 31, 2017 |
|
|
Encumbered |
Unencumbered |
|
|
Note |
|
Pledged as
collateral
Rs. ’000 |
Other
Rs. ’000 |
Available as
collateral
Rs. ’000 |
Other
Rs. ’000 |
Total
Rs. ’000 |
| Cash and cash equivalents |
27 |
|
|
|
33,224,619 |
|
33,224,619 |
| Balances with central banks |
28 |
|
|
39,766,630 |
5,034,816 |
|
44,801,446 |
| Placements with banks |
29 |
|
|
|
17,633,269 |
|
17,633,269 |
| Securities purchased under resale agreements |
|
|
|
|
|
|
– |
| Derivative financial assets |
30 |
|
|
|
2,334,536 |
|
2,334,536 |
| Other financial instruments – Held for trading |
31 |
|
|
|
4,410,913 |
|
4,410,913 |
| Loans and receivables to banks* |
32 |
|
|
640,512 |
|
|
640,512 |
| Loans and receivables to other customers |
33 |
|
|
|
737,446,567 |
|
737,446,567 |
| Financial investments – Available for sale** |
34 |
|
58,768,665 |
|
95,945,467 |
|
154,714,132 |
| Financial investments – Held to maturity |
35 |
|
|
|
63,562,752 |
|
63,562,752 |
| Financial investments – Loans and receivables |
36 |
|
|
|
48,712,477 |
|
48,712,477 |
| Total |
|
|
58,768,665 |
40,407,142 |
1,008,305,416 |
– |
1,107,481,223 |
| As at December 31, 2016 |
|
|
Encumbered |
Unencumbered |
|
|
Note |
|
Pledged as
collateral
Rs. ’000 |
Other
Rs. ’000 |
Available as
collateral
Rs. ’000 |
Other
Rs. ’000 |
Total
Rs. ’000 |
| Cash and cash equivalents |
27 |
|
|
|
30,193,589 |
|
30,193,589 |
| Balances with central banks |
28 |
|
|
34,268,658 |
9,604,547 |
|
43,873,205 |
| Placements with banks |
29 |
|
|
|
11,718,499 |
|
11,718,499 |
| Securities purchased under resale agreements |
|
|
|
|
|
|
– |
| Derivative financial assets |
30 |
|
|
|
1,052,829 |
|
1,052,829 |
| Other financial instruments – Held for trading |
31 |
|
|
|
4,987,798 |
|
4,987,798 |
| Loans and receivables to banks * |
32 |
|
|
624,458 |
|
|
624,458 |
| Loans and receivables to other customers |
33 |
|
|
|
616,018,228 |
|
616,018,228 |
| Financial investments – Available for sale** |
34 |
|
89,037,472 |
|
70,985,999 |
|
160,023,471 |
| Financial investments – Held to maturity |
35 |
|
|
|
60,981,298 |
|
60,981,298 |
| Financial investments – Loans and receivables |
36 |
|
|
|
51,824,026 |
|
51,824,026 |
| Total |
|
|
89,037,472 |
34,893,116 |
857,366,813 |
– |
981,297,401 |
*Represents an amount where the Bank is prevented from exercising the right of lien against the claim made by the Bank due to a Court action.
** Market value of securities pledged as collateral is considered as encumbered.
69.3 Market risk
Market risk is the risk of losses in On or Off-Balance Sheet positions arising out of movements in prices affecting foreign exchange exposures, interest rate instruments, equity/debt instruments and commodity exposures. The Bank monitors market risk in both trading and non-trading portfolios.
69.3.1 Exposure to market risk – trading and non-trading portfolios
The table below sets out the allocation of assets and liabilities subject to market risk between trading and non-trading portfolios:
| As at December 31, 2017 |
|
|
|
Market risk measurement |
|
Note |
|
Carrying amount
Rs. ’000 |
Trading portfolios
Rs. ’000 |
Non-trading
portfolios
Rs. ’000 |
| Assets subject to market risk |
|
|
|
|
|
| Cash and cash equivalents |
27 |
|
12,387,967 |
|
12,387,967 |
| Balances with central banks |
28 |
|
4,601,606 |
|
4,601,606 |
| Placements with banks |
29 |
|
17,633,269 |
|
17,633,269 |
| Derivative financial assets |
30 |
|
2,334,536 |
2,334,536 |
– |
| Other financial instruments – Held for trading |
31 |
|
4,410,913 |
4,410,913 |
– |
| Loans and receivables to banks |
32 |
|
640,512 |
|
640,512 |
| Loans and receivables to other customers |
33 |
|
737,446,567 |
|
737,446,567 |
| Financial investments – Available for sale |
34 |
|
154,714,132 |
|
154,714,132 |
| Financial investments – Held to maturity |
35 |
|
63,562,752 |
|
63,562,752 |
| Financial investments – Loans and receivables |
36 |
|
48,712,477 |
|
48,712,477 |
| Total |
|
|
1,046,444,731 |
6,745,449 |
1,039,699,282 |
| Liabilities subject to market risk |
|
|
|
|
|
| Due to banks |
43 |
|
57,120,991 |
|
57,120,991 |
| Derivative financial liabilities |
44 |
|
3,678,494 |
3,678,494 |
|
| Securities sold under repurchase agreements |
|
|
49,676,767 |
|
49,676,767 |
| Due to other customers/deposits from customers |
45 |
|
807,630,072 |
|
807,630,072 |
| Other borrowings |
46 |
|
23,786,094 |
|
23,786,094 |
| Subordinated liabilities |
52 |
|
25,165,924 |
|
25,165,924 |
| Total |
|
|
967,058,342 |
3,678,494 |
963,379,848 |
| As at December 31, 2016 |
|
|
|
Market risk measurement |
|
Note |
|
Carrying amount
Rs. ’000 |
Trading portfolios
Rs. ’000 |
Non-trading
portfolios
Rs. ’000 |
| Assets subject to market risk |
|
|
|
|
|
| Cash and cash equivalents |
27 |
|
14,704,722 |
|
14,704,722 |
| Balances with central banks |
28 |
|
3,403,219 |
|
3,403,219 |
| Placements with banks |
29 |
|
11,718,499 |
|
11,718,499 |
| Derivative financial assets |
30 |
|
1,052,829 |
1,052,829 |
|
| Other financial instruments – Held for trading |
31 |
|
4,987,798 |
4,987,798 |
|
| Loans and receivables to banks |
32 |
|
624,458 |
|
624,458 |
| Loans and receivables to other customers |
33 |
|
616,018,228 |
|
616,018,228 |
| Financial investments – Available for sale |
34 |
|
160,023,471 |
|
160,023,471 |
| Financial investments – Held to maturity |
35 |
|
60,981,298 |
|
60,981,298 |
| Financial investments – Loans and receivables |
36 |
|
51,824,026 |
|
51,824,026 |
| Total |
|
|
925,338,548 |
6,040,627 |
919,297,921 |
| Liabilities subject to market risk |
|
|
|
|
|
| Due to banks |
43 |
|
67,608,811 |
|
67,608,811 |
| Derivative financial liabilities |
44 |
|
1,515,035 |
1,515,035 |
|
| Securities sold under repurchase agreements |
|
|
69,867,469 |
|
69,867,469 |
| Due to other customers/deposits from customers |
45 |
|
701,410,848 |
|
701,410,848 |
| Other borrowings |
46 |
|
9,270,154 |
|
9,270,154 |
| Subordinated liabilities |
52 |
|
24,849,539 |
|
24,849,539 |
| Total |
|
|
874,521,856 |
1,515,035 |
873,006,821 |
69.3.2 Exposure to interest rate risk – Sensitivity analysis
69.3.2 (a) Exposure to interest rate risk – Non-trading portfolio
The possibility that changes in interest rates will affect future cash flows or the fair values of financial instruments gives rise to interest rate risk. The Bank’s policy is to continuously monitor portfolios and adopt hedging strategies to ensure that interest rate risk is maintained within prudent levels.
The tables below analyse the Bank’s interest rate risk exposure on financial assets and financial liabilities. The Bank’s assets and liabilities are included at carrying amounts and categorised by the earlier of contractual re-pricing or maturity dates.
Interest rate gap position of the non-trading portfolio of the Bank is given below:
| As at December 31, 2017 |
Up to 3
months |
3 to 12
months |
1 to 3
years |
3 to 5
years |
More than
5 years |
Non-
sensitive |
Total as at
31.12.2017 |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Financial assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Cash and cash equivalents |
3,952,578 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
29,272,041 |
33,224,619 |
| Balances with central banks |
4,601,606 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
40,199,840 |
44,801,446 |
| Placements with banks |
16,097,269 |
1,536,000 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
17,633,269 |
Securities purchased under
resale agreements |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Derivative financial assets |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Other financial instruments –
Held for trading |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Loans and receivables to banks |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
640,512 |
640,512 |
| Loans and receivables to other customers |
460,905,113 |
134,400,971 |
65,554,128 |
38,341,792 |
31,537,815 |
6,706,748 |
737,446,567 |
| Financial investments – Available for sale |
10,573,104 |
68,317,215 |
46,631,198 |
28,638,006 |
– |
554,609 |
154,714,132 |
| Financial investments – Held to maturity |
4,077,406 |
9,871,844 |
12,885,242 |
29,661,660 |
7,066,600 |
– |
63,562,752 |
Financial investments –
Loans and receivables |
41,140,625 |
1,893,522 |
5,678,330 |
– |
– |
– |
48,712,477 |
| Total financial assets |
541,347,701 |
216,019,552 |
130,748,898 |
96,641,458 |
38,604,415 |
77,373,750 |
1,100,735,774 |
| Financial liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Due to banks |
44,703,696 |
5,366,253 |
– |
– |
– |
7,051,042 |
57,120,991 |
| Derivative financial liabilities |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Securities sold under repurchase agreements |
35,949,554 |
10,652,592 |
2,733,779 |
– |
– |
340,842 |
49,676,767 |
Due to other customers/deposits
from customers |
457,830,953 |
286,182,073 |
16,482,261 |
12,360,297 |
10,739,911 |
66,532,016 |
850,127,511 |
| Other borrowings |
18,293,434 |
814,083 |
1,002,777 |
908,493 |
2,767,307 |
– |
23,786,094 |
| Subordinated liabilities |
11,664,201 |
327,156 |
– |
9,500,724 |
3,673,843 |
– |
25,165,924 |
| Total financial liabilities |
568,441,838 |
303,342,157 |
20,218,817 |
22,769,514 |
17,181,061 |
73,923,900 |
1,005,877,287 |
| Interest rate sensitivity gap |
(27,094,137) |
(87,322,605) |
110,530,081 |
73,871,944 |
21,423,354 |
3,449,850 |
94,858,487 |
| As at December 31, 2016 |
Up to 3
months |
3 to 12
months |
1 to 3
years |
3 to 5
years |
More than
5 years |
Non-
sensitive |
Total as at
31.12.2016 |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Financial assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Cash and cash equivalents |
6,991,886 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
23,201,703 |
30,193,589 |
| Balances with central banks |
3,403,219 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
40,469,986 |
43,873,205 |
| Placements with banks |
11,718,499 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
11,718,499 |
| Securities purchased under resale agreements |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Derivative financial assets |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Other financial instruments –
Held for trading |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Loans and receivables to banks |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
624,458 |
624,458 |
| Loans and receivables to other customers |
380,578,852 |
114,228,759 |
56,281,391 |
30,331,334 |
29,613,153 |
4,984,739 |
616,018,228 |
| Financial investments – Available for sale |
4,616,318 |
35,445,896 |
94,598,716 |
24,912,386 |
– |
450,155 |
160,023,471 |
| Financial investments – Held to maturity |
13,220,906 |
5,077,400 |
17,061,858 |
135,192 |
25,485,942 |
– |
60,981,298 |
Financial investments –
Loans and receivables |
41,332,775 |
2,599,730 |
5,663,994 |
2,227,527 |
– |
– |
51,824,026 |
| Total financial assets |
461,862,455 |
157,351,785 |
173,605,959 |
57,606,439 |
55,099,095 |
69,731,041 |
975,256,774 |
| Financial liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Due to banks |
47,523,006 |
17,370,999 |
– |
– |
– |
2,714,806 |
67,608,811 |
| Derivative financial liabilities |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Securities sold under repurchase agreements |
55,479,230 |
14,377,545 |
10,694 |
– |
– |
– |
69,867,469 |
Due to other customers/deposits
from customers |
419,615,132 |
229,599,655 |
14,761,841 |
10,500,371 |
8,882,763 |
56,203,732 |
739,563,494 |
| Other borrowings |
5,601,711 |
322,650 |
661,989 |
639,217 |
2,044,587 |
– |
9,270,154 |
| Subordinated liabilities |
11,670,109 |
– |
– |
9,502,140 |
3,677,290 |
– |
24,849,539 |
| Total financial liabilities |
539,889,188 |
261,670,849 |
15,434,524 |
20,641,728 |
14,604,640 |
58,918,538 |
911,159,467 |
| Interest rate sensitivity gap |
(78,026,733) |
(104,319,064) |
158,171,435 |
36,964,711 |
40,494,455 |
10,812,503 |
64,097,307 |
69.3.2 (b) Exposure to interest rate risk – non-trading portfolio (rate shocks)
The management of interest rate risk against interest rate gap limits is supplemented by monitoring the sensitivity of the Bank’s financial assets and financial liabilities to various interest rate scenarios.
The following table demonstrates the sensitivity of the Bank’s Income Statement as at the reporting date to a reasonably possible change in interest rates, with all other variables held constant.
Sensitivity of projected net interest income
|
2017 |
2016 |
| Net interest income (NII) |
Parallel increase
Rs. ’000 |
Parallel decrease
Rs. ’000 |
Parallel increase
Rs. ’000 |
Parallel decrease
Rs. ’000 |
| As at December 31, |
1,243,611 |
(1,241,623) |
670,859 |
(668,620) |
| Average for the period |
920,414 |
(918,225) |
634,306 |
(632,375) |
| Maximum for the period |
1,243,611 |
(1,241,623) |
827,488 |
(824,962) |
| Minimum for the period |
706,442 |
(704,325) |
366,432 |
(365,569) |
The graph below depicts the impact on the Net Interest Income due to a rate shock of 100 bps on Rupee denominated assets and liabilities and 25 bps on FCY denominated Assets and Liabilities.
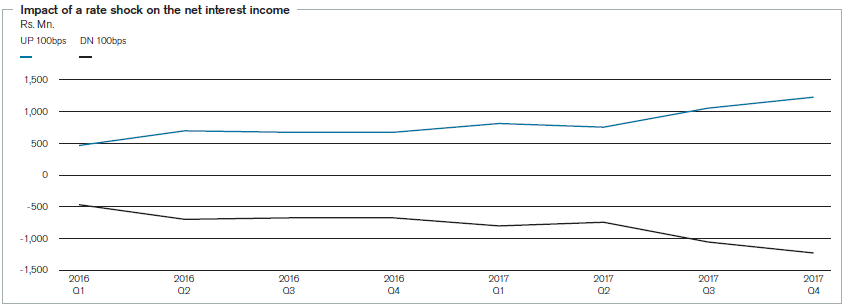
The impact of changes in interest rates on NII is measured applying interest rate shocks on static Balance Sheet. In line with the industry practices, interest rate shock of 100 bps is applied on LKR denominated assets and liabilities and 25 bps on FCN denominated assets and liabilities. The potential impact on the Bank’s profitability due to changes in Rupee and Foreign currency interest rates is evaluated to ensure that the volatilities are prudently managed within the internal tolerance limits. Above graph depicts the sensitivity of NII to rate shocks during the years 2016 and 2017. Since the first quarter of 2017, the impact of rate shocks on projected NII has been gradually increasing due to the conscious decision of the Bank to focus more on short-term Fixed Income Securities (FIS) portfolio, considering the prevailed market conditions.
69.3.3 Exposure to currency risk – Non-trading portfolio
Currency risk arises as a result of fluctuations in the value of a financial instrument due to changes in foreign exchange rates. There are set limits on position by currency and these positions are monitored on a daily basis.
The table below indicates the currencies to which the Bank had significant exposures as at December 31, 2017 and 2016 and the exposure as a percentage of the total capital funds:
Foreign Exchange Position as at December 31, 2017
| Currency |
Spot |
Forward |
Net open
position |
Net position
in other
exchange
contracts |
Overall
exposure in
respective
foreign
currency |
Overall
exposure
in Rs. |
|
Assets |
Liabilities |
Net |
Assets |
Liabilities |
Net |
|
2
’000 |
3
’000 |
4=2-3
’000 |
5
’000 |
6
’000 |
7=5-6
’000 |
8
’000 |
9
’000 |
10
’000 |
11
’000 |
| United States Dollar |
22,289 |
22,822 |
(533) |
5,350 |
389 |
4,961 |
2,734 |
– |
7,162 |
1,100,083 |
| Great Britain Pound |
388 |
473 |
(85) |
36 |
– |
36 |
20 |
– |
(29) |
(5,991) |
| Euro |
5,479 |
5,696 |
(217) |
– |
– |
– |
(52) |
– |
(269) |
(49,344) |
| Japanese Yen |
12,181 |
8,754 |
3,427 |
11,278 |
18,042 |
(6,764) |
372 |
– |
(2,965) |
(4,039) |
| Indian Rupee |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Australian Dollar |
482 |
633 |
(151) |
106 |
16 |
90 |
10 |
– |
(51) |
(6,106) |
| Canadian Dollar |
65 |
13 |
52 |
– |
– |
– |
(34) |
– |
18 |
2,201 |
Other currencies in
US Dollars |
705 |
354 |
351 |
– |
170 |
(170) |
(88) |
– |
93 |
14,285 |
| Total exposure |
|
|
|
|
|
|
USD 2,595 |
|
USD 6,843 |
1,051,089 |
Total capital funds as per the Audited Basel llI computation
(capital base of the Bank as at December 31, 2017) |
|
|
|
|
122,415,882 |
| Total exposure as a percentage of total capital funds (%) |
|
|
|
0.86 |
Foreign exchange position as at December 31, 2016
| Currency |
Spot |
Forward |
Net open
position |
Net position
in other
exchange
contracts |
Overall
exposure in
respective
foreign
currency |
Overall
exposure
in Rs. |
|
Assets |
Liabilities |
Net |
Assets |
Liabilities |
Net |
|
2
’000 |
3
’000 |
4=2-3
’000 |
5
’000 |
6
’000 |
7=5-6
’000 |
8
’000 |
9
’000 |
10
’000 |
11
’000 |
| United States Dollar |
34,367 |
42,279 |
(7,912) |
20,447 |
11,005 |
9,442 |
3,179 |
|
4,709 |
705,226 |
| Great Britain Pound |
3,524 |
7,832 |
(4,308) |
5,072 |
807 |
4,265 |
45 |
|
3 |
467 |
| Euro |
5,216 |
5,384 |
(168) |
420 |
300 |
120 |
66 |
|
17 |
2,703 |
| Japanese Yen |
15,549 |
2,271 |
13,278 |
5,847 |
18,937 |
(13,090) |
(150) |
|
38 |
49 |
| Indian Rupee |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
|
– |
– |
| Australian Dollar |
180 |
71 |
109 |
– |
100 |
(100) |
(40) |
|
(30) |
(3,284) |
| Canadian Dollar |
97 |
74 |
23 |
– |
– |
– |
(1) |
|
23 |
2,538 |
Other currencies in
US Dollars |
914 |
340 |
574 |
– |
509 |
(509) |
95 |
|
160 |
23,948 |
| Total exposure |
|
|
|
|
|
|
USD 3,367 |
|
USD 4,886 |
731,647 |
Total capital funds as per the Audited Basel llI computation
(capital base of the Bank as at December 31, 2016) |
|
|
|
|
96,517,086 |
| Total exposure as a percentage of total capital funds (%) |
|
|
|
0.76 |
The Bank regularly conducts sensitivity analysis on Net Open Position (NOP) due to possible changes in the USD/LKR exchange rate to assess the exposure to Foreign Exchange (FX) Risk. An appropriate shock based on historical USD/LKR exchange rate is applied on the NOP which is measured against the Board approved threshold limits.
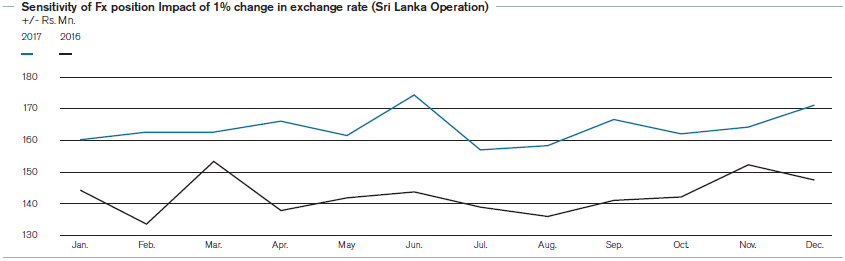
69.3.4 Exposure to equity price risk
Equity price risk arises as a result of any change in prices and volatilities of individual equities. The Bank conducts mark-to-market calculations on a daily, quarterly and on a need basis to identify the impact due to changes in equity prices.
Impact on Income Statement due to a change in market price by 10% on equity shares held by the Bank.
The table below summarises the impact (both to the Income Statement and to the equity) due to a shock of 10% on equity prices.
|
2017 |
2016 |
|
Held for trading
Rs. ’000 |
Available for sale
Rs. ’000 |
Total
Rs. ’000 |
Held for trading
Rs. ’000 |
Available for sale
Rs. ’000 |
Total
Rs. ’000 |
Market value of equity securities
as at December 31, |
314,745 |
500,278 |
815,023 |
293,809 |
246,548 |
540,357 |
| Stress Level |
Impact on P&L |
Impact on OCI |
Impact on equity |
Impact on P&L |
Impact on OCI |
Impact on Equity |
| Shock of 10% on equity prices (upward) |
31,475 |
50,028 |
81,503 |
29,381 |
24,655 |
54,036 |
| Shock of 10% on equity prices (downward) |
(31,475) |
(50,028) |
(81,503) |
(29,381) |
(24,655) |
(54,036) |
69.4 Operational risk
Operational risk arises due to inadequate or failed internal processes, people and systems or from external events. Operational risk events which include legal and regulatory implications could lead to financial and reputational losses to the Bank.
The Operational Risk Management framework of the Bank has been defined under the Board approved Operational Risk Management Policy. Operational risk is managed by establishing an appropriate internal control system that requires a mechanism for segregation of related responsibilities within the Bank, and a detailed testing and verification of the Bank’s overall operational systems, and achieving a full harmony between internal and external systems and establishing a fully independent back-up facility for business continuity planning.
69.5 Capital management and Pillar III disclosures as per Basel III
Objective
The Bank is required to manage its capital taking into account the need to meet the regulatory requirements as well as the current and future business needs, stakeholder expectations and available options for raising capital.
69.5.1 Regulatory capital
Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) is calculated based on the CBSL Directions stemming from Basel III Accord. These guidelines require the Bank to maintain a CAR not less than 7.75% with minimum Tier 1 Capital with buffers in relation to total risk weighted assets and a minimum Total CAR of 11.75% with buffers in relation to total risk weighted assets as at December 31, 2017.
| As at December 31, |
2017 |
2016 |
|
Rs. ’000 |
Rs. ’000 |
| Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1) Capital after adjustments |
94,151,253 |
67,284,572 |
| Total Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1) Capital |
96,696,269 |
69,368,825 |
| Equity capital (stated capital)/assigned capital |
37,143,541 |
24,977,700 |
| Reserve fund |
6,476,952 |
5,647,890 |
| Published retained earnings/(accumulated retained losses) |
1,798,112 |
1,538,142 |
| Published Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (OCI) |
(1,522,156) |
(6,705,188) |
| General and other disclosed reserves |
52,799,820 |
43,910,281 |
| Unpublished current year's profit/(losses) and gains reflected in OCI |
– |
– |
| Ordinary shares issued by consolidated banking and financial subsidiaries of the bank and held by third parties |
– |
– |
| Total adjustments to CET1 Capital |
2,545,016 |
2,084,253 |
| Goodwill (net) |
– |
– |
| Intangible assets (net) |
776,812 |
640,646 |
| Revaluation losses of property, plant and equipment |
3,813 |
– |
| Significant investments in the capital of financial institutions where the bank owns more than 10 per cent of the issued ordinary share capital of the entity |
1,764,391 |
1,443,607 |
| Additional Tier 1 (AT1) Capital after adjustments |
– |
– |
| Total additional Tier 1 (ATI) Capital |
– |
– |
| Qualifying additional Tier 1 capital instruments |
– |
– |
| Instruments issued by consolidated banking and financial subsidiaries of the Bank and held by third parties |
– |
– |
| Total adjustments to AT1 Capital |
– |
– |
| Investment in own shares |
– |
– |
| Others (Specify) |
– |
– |
| Tier 2 Capital after adjustments |
28,264,629 |
29,232,514 |
| Total Tier 2 Capital |
28,264,629 |
29,232,514 |
| Qualifying Tier 2 capital instruments |
22,799,002 |
24,334,875 |
| Revaluation gains |
2,024,804 |
2,034,231 |
| Loan loss provisions |
3,440,823 |
2,863,408 |
| Instruments issued by Consolidated Banking and Financial Subsidiaries of the Bank and held by Third Parties |
– |
– |
| Total adjustments to Tier 2 capital |
– |
– |
| Investment in own shares |
– |
– |
| Others (Specify) |
– |
– |
| CET1 capital |
94,151,253 |
67,284,572 |
| Total Tier 1 capital |
94,151,253 |
67,284,572 |
| Total Capital |
122,415,882 |
96,517,086 |
69.5.2 Capital allocation
Management monitors the capital adequacy ratio on a regular basis and ensure that it operates well above the internal limit set by the Bank. The allocation of capital between specific operations and activities, to a large extent, driven by optimisation of the return on the capital allocated. The amount of capital allocated to each operation or activity is based primarily on regulatory capital requirements, but in some cases the regulatory requirements do not fully reflect the varying degree of risk associated with different activities. In such cases, the capital requirements may be flexed to reflect differing risk profiles, subject to the overall level of capital to support a particular operation or activity not falling below the minimum required level by the regulator.
69.5.3 Pillar III disclosures as per Basel III
Disclosure under these requirements mainly include the regulatory capital requirements and liquidity, risk weighted assets, discussion on adequacy to meet current and future capital requirements of banks and linkages between financial statements and regulatory exposures. It is required to disclosure the templates specified by the Central Bank of Sri Lanka as per Basel III - Minimum disclosure requirements with effective from July 01, 2017.
70. Events After the Reporting Period
No circumstances have arisen since the reporting date which would require adjustments or disclosure in the Financial Statements other than disclosed below:
70.1 Interim dividend – 2017
The Bank declared and paid a second interim dividend of Rs. 3/- per share on February 20, 2018 to both the voting and non-voting ordinary shareholders of the Bank, for the year ended December 31, 2017.
In accordance with the Sri Lanka Accounting Standard – LKAS 10 on “Events After the Reporting Period”, this second interim dividend has not been recognised as a liability as at December 31, 2017. Under the Inland Revenue Act No. 10 of 2006, a withholding tax of 10% has been imposed on dividends paid.
70.2 Final dividend – 2017
The Board of Directors of the Bank has recommended the payment of a final dividend of Rs. 2/- per share which will be satisfied in the form of issue and allotment of new shares for both the voting and non-voting ordinary shareholders of the Bank for the year ended December 31, 2017.
This final dividend is yet to be approved at the Annual General Meeting to be held on March 28, 2018. In accordance with the Sri Lanka Accounting Standard – LKAS 10 on “Events After the Reporting Period”, this proposed final dividend has not been recognised as a liability as at December 31, 2017. Under the Inland Revenue Act No. 10 of 2006, a withholding tax of 10% has been imposed on dividends declared.
Compliance with Sections 56 and 57 of Companies Act No. 07 of 2007
As required by the Section 56 of the Companies Act No. 07 of 2007, the Board of Directors of the Bank satisfied the solvency test in accordance with the Section 57, prior to recommending the final dividend. A Statement of Solvency completed and duly signed by
the Directors on February 23, 2018 has been audited by Messrs KPMG.








